Date Added (newest)


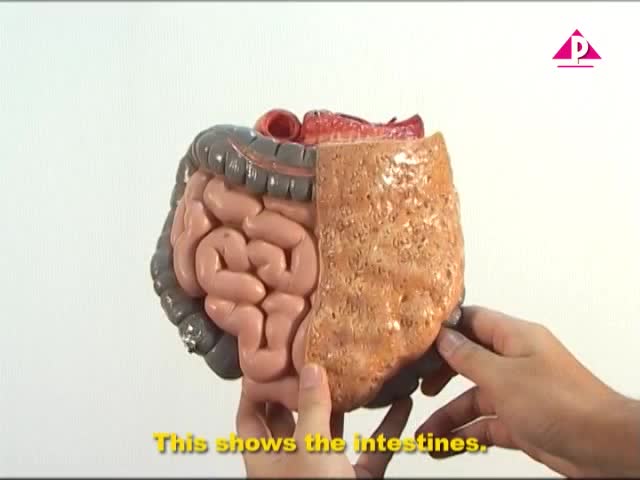
Human Digestive System for Testing The Video System
Free


Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
Free


S3 IS Exp Amylase
Free


S3 IS Expt Protease
Free


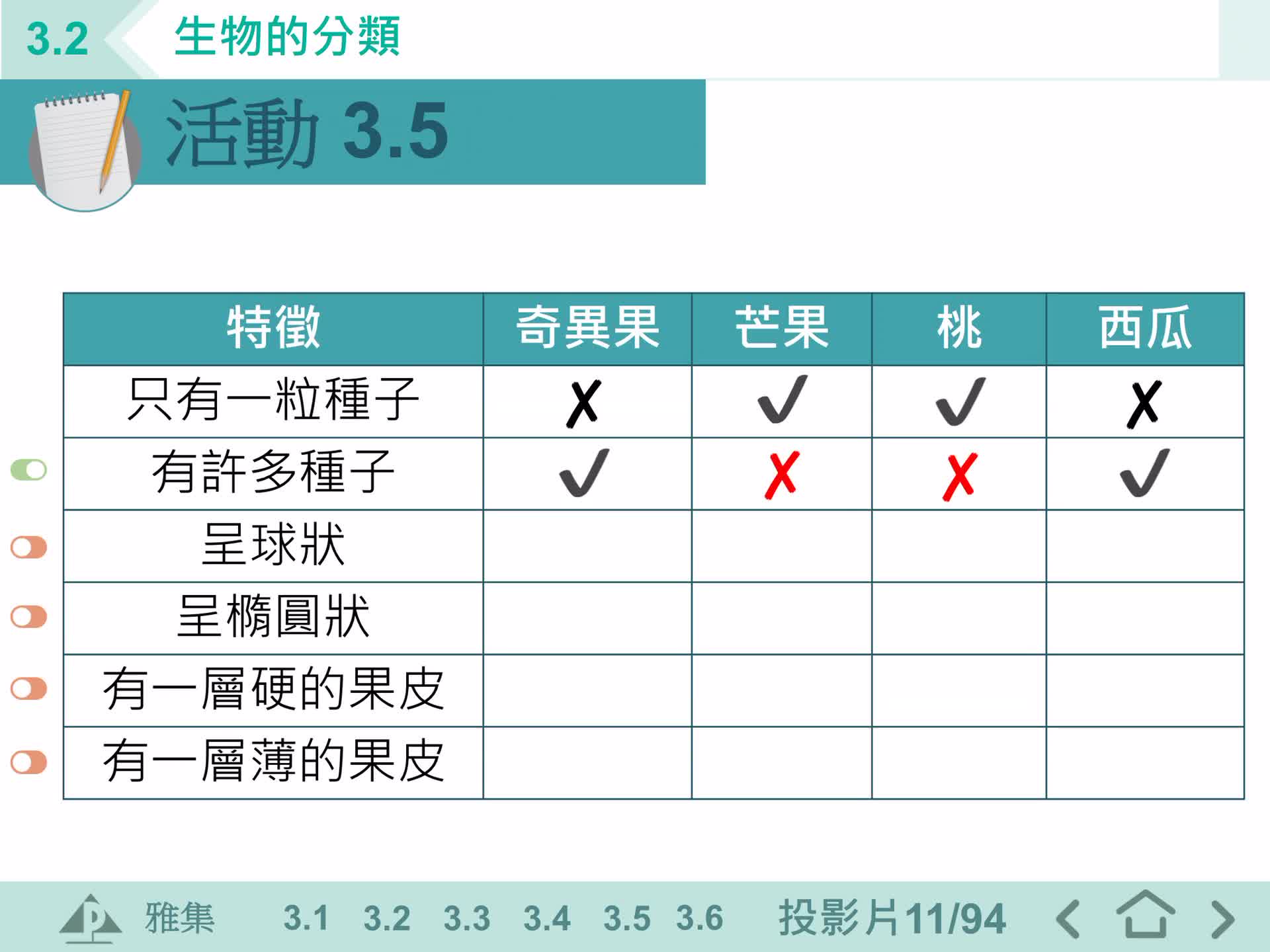
S1 IS 植物分類


S1 IS 脊椎動物分類


S1 IS 動物分類


S1 IS 檢索表


Note P.4-5


How to use schoology


LeeYu F1 IS 3.3生物與生境


3.4 生物多樣性


3.6保育


3.5生物多樣性減少


LEE YU S1 Ch6.1C


LEE YU S1 Ch6.1AB


LEEYU F1 6.2A


LEE YU F1 Ch6.2B


LEE YU F1 Ch6.4B


LEE YU F1 Ch6.4A
Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
652 0 05-Science Free
In this video we discuss the structure of the stomach and the functions of the stomach. We cover the sections of the stomach and the different cells that make up the gastric pits in the stomach. Transcript/notes Stomach Your stomach is an organ that has many important roles in bodily functions. The stomach is like a holding sack as between 3 to 4 liters of food and drink enters it daily. These items typically spend 2 to 6 hours there before being passed on to the small intestine. The stomach is a J shaped organ located in the abdomen. When you chew food, then swallow it, it enters your esophagus, which connects with and passes the food to your stomach. The stomach is typically divided into 4 sections. The Cardia is the entryway to the stomach, near where the stomach and esophagus meet. The Fundus is the dome shaped region located above and to the left of where the stomach and esophagus meet. The body is the largest region of the stomach and it extends to the 4th section of the stomach, the pylorus. The pylorus is a funnel shaped region that connects the stomach to the duodenum of the small intestine. The inner lining of the stomach has a rough appearance made by gastric folds. These gastric folds have gastric pits which contain gastric glands. These glands secrete most of the gastric juice released in the stomach and this juice is a mucous fluid that contains mainly digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid. There are 5 types of secretory cells that are located in the gastric epithelium. Surface mucous cells line the inner stomach and extend into the gastric pits and they secrete an alkaline fluid containing mucin that helps protect the stomach lining from exposure to the high acidity of gastric juices and gastric enzymes. Mucous neck cells are located deeper than the surface cells and they secrete an acidic mucin and which helps to maintain acidic conditions. Parietal cells produce hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor binds to vitamin B12 molecules and protects them from digestive juices until they reach the small intestine. Hydrochloric acid is not actually produced in the cells, as it forms form positive hydrogen ions and negative chlorine ions secreted from the cells. Hydrochloric acid is responsible for the low pH level in the stomach. Hcl is important in enzyme activation, unfolding certain proteins and it also protects against many microorganisms. Chief cells produce pepsinogen, which is the precursor to the enzyme pepsin. Pepsin is activated by hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and it digests or breaks down proteins into smaller peptide fragments. Chief cells also produce gastric lipase which is an enzyme that aids in the digestion of fats. G cells release gastrin into blood, which stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen, ensuring that there are enough digestive enzymes when food is present in the stomach. The outer stomach wall is comprised of 3 layers of smooth muscle tissue, an oblique muscle layer, a circular muscle layer, and a longitudinal layer, with a serosa being the outermost layer. The stomach has several important functions in your body, as it serves as a food reservoir, storing food until it can be moved into the small intestine. As we have covered, it releases gastric juice, which contains enzymes that take part in the digestion of food. The stomach actually churns food, breaking it down into smaller particles and mixing them with the gastric juice. It secretes intrinsic factor, which protects vitamin B12 molecules, which are important in cell metabolism. The stomach absorbs some alcohol, aspirin, and some short chain fatty acids. And the stomach produces gastrin to help regulate digestive functions.
Most popular


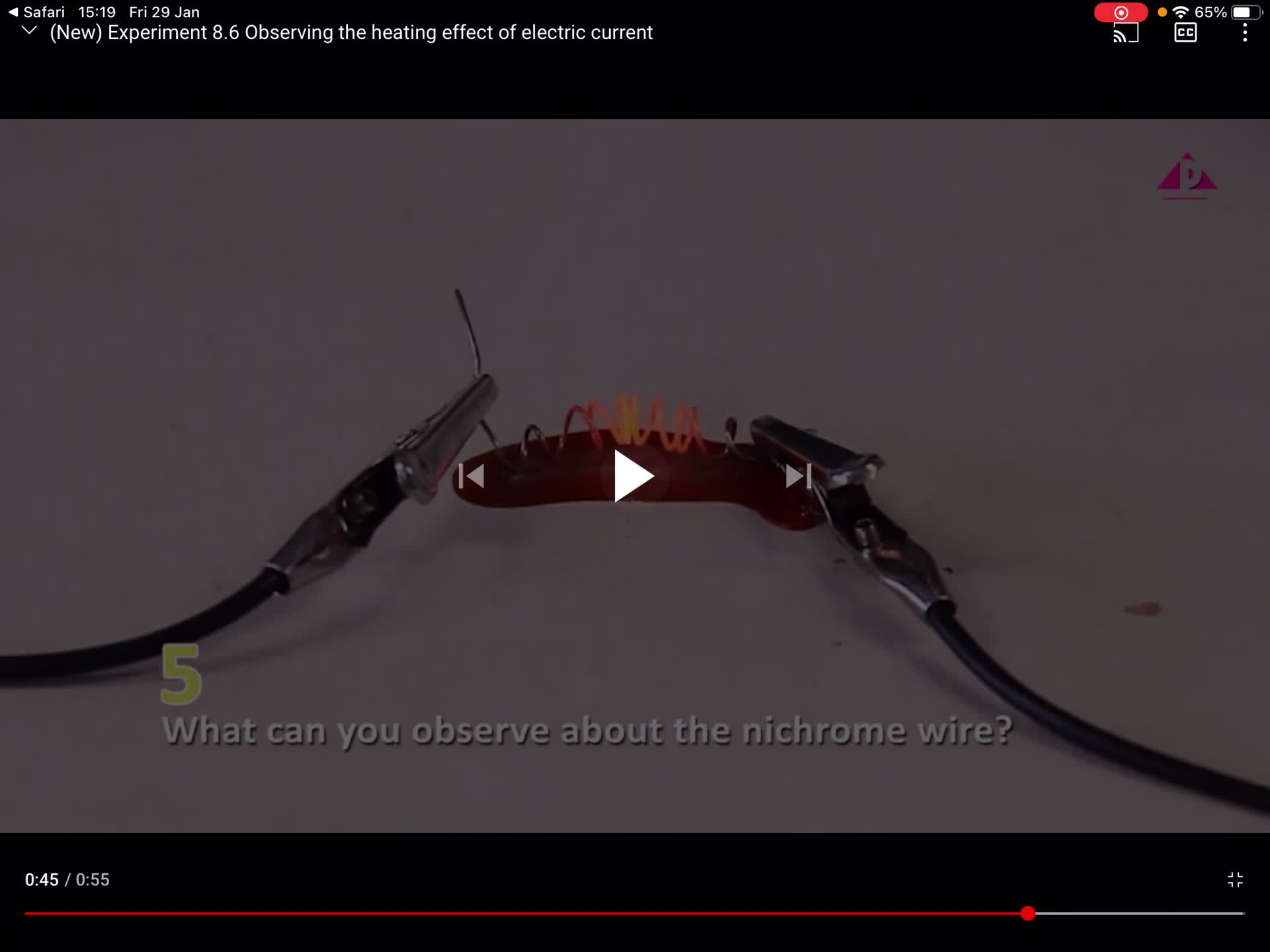
2D IS Unit 8 Section 8.8 Part B & C
Free


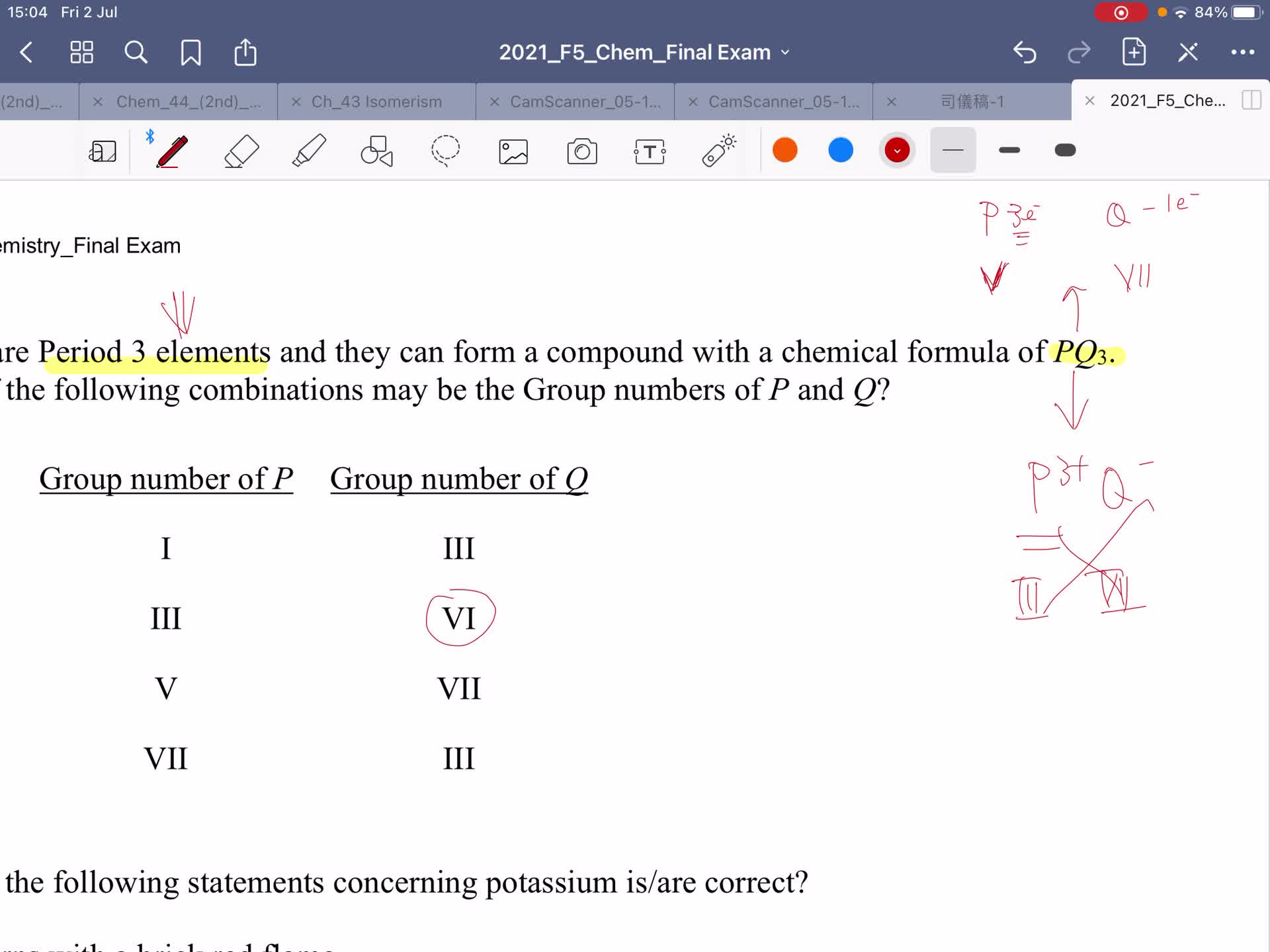
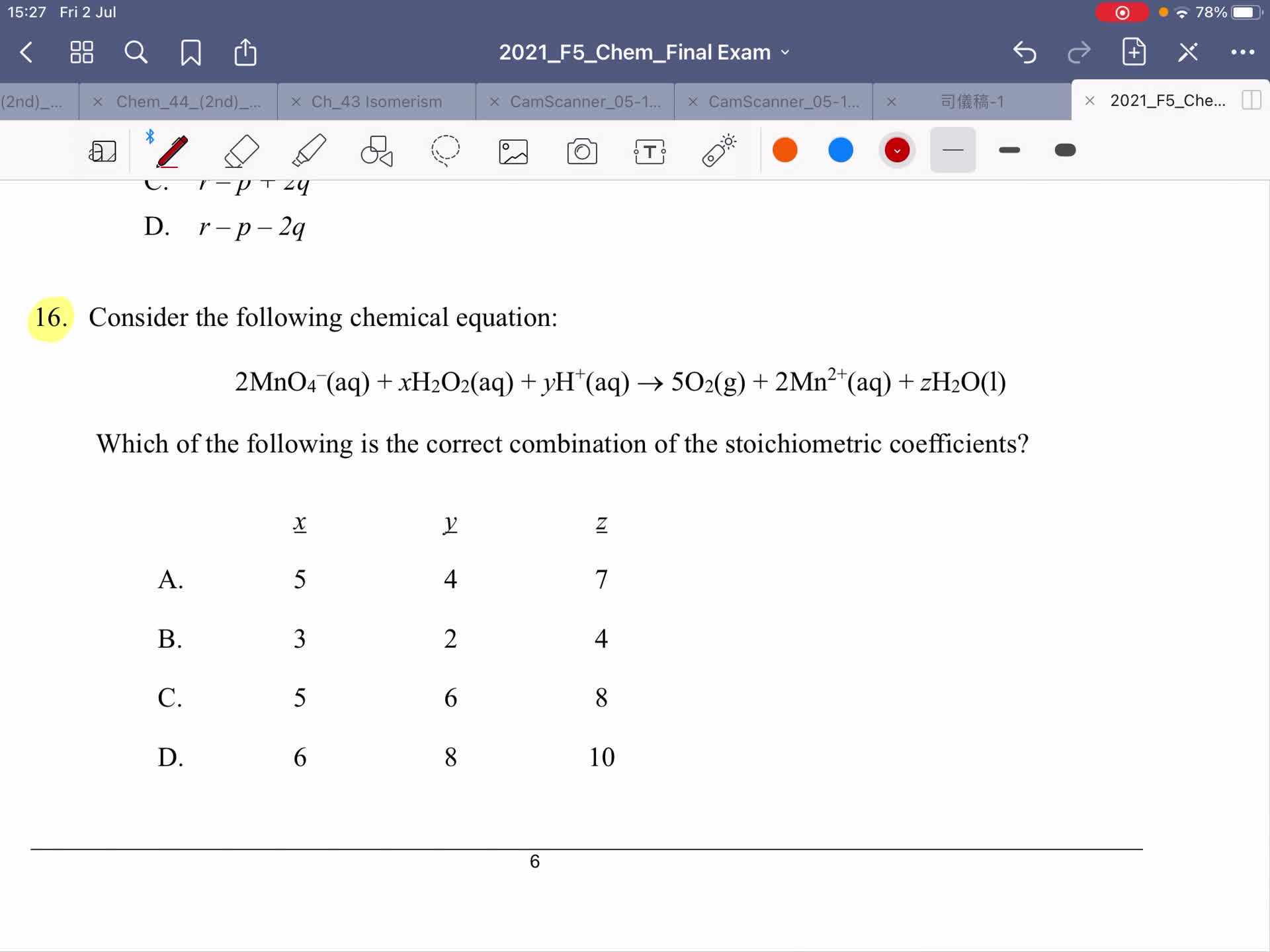
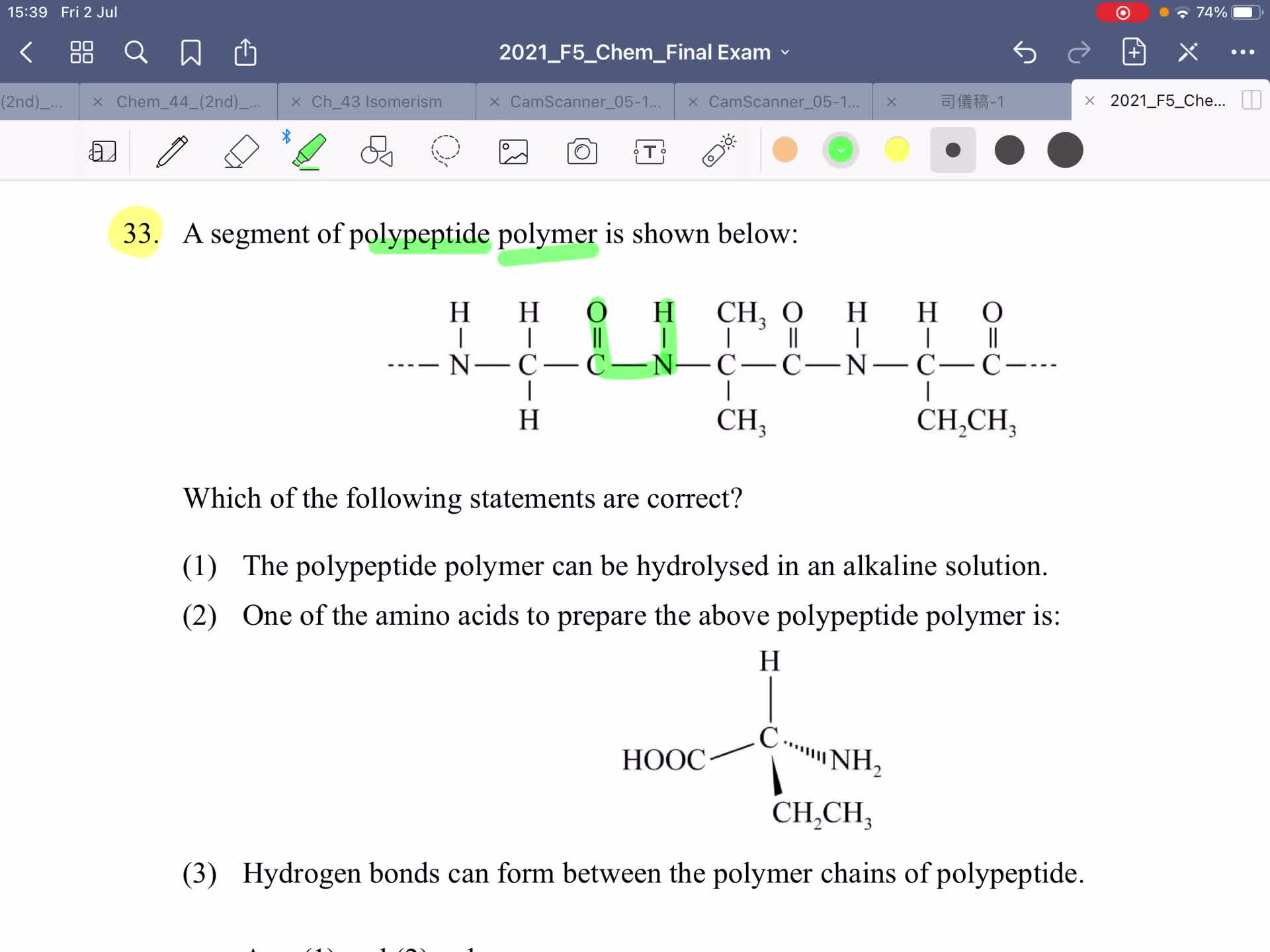
2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 1
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 2
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 3
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.2 Observing ox eye cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.1 Using a microscope
Free


F1 IS 6.6 C Floating and sinking
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 2)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 A & C Air & Application of gas
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 2)
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household electricity (Part 1)
Free


F1 IS 5.3C Radiation (Part 2)
Free


F1 IS 5.3C Radiation (Part 1)
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section C Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section C Part 1
Free


F1 IS 5.3A Convection (Part 2)
Free
Most watched


Human Digestive System for Testing The Video System
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 2)
Free


F1 IS 6.6 C Floating and sinking
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 1
Free


(New) Experiment 4.2 Observing ox eye cells with a microscope
Free


F2 IS 7.1 A & C Air & Application of gas
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household electricity (Part 1)
Free


2D IS Unit 8 Section 8.8 Part B & C
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 3
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 2)
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 2
Free


S3 IS Expt Protease
Free


(New) Experiment 4.1 Using a microscope
Free


S3 IS Exp Amylase
Free


Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
Free


F2 IS Ch.8 WB 對答案
Free
Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
652 0 05-Science Free

In this video we discuss the structure of the stomach and the functions of the stomach. We cover the sections of the stomach and the different cells that make up the gastric pits in the stomach. Transcript/notes Stomach Your stomach is an organ that has many important roles in bodily functions. The stomach is like a holding sack as between 3 to 4 liters of food and drink enters it daily. These items typically spend 2 to 6 hours there before being passed on to the small intestine. The stomach is a J shaped organ located in the abdomen. When you chew food, then swallow it, it enters your esophagus, which connects with and passes the food to your stomach. The stomach is typically divided into 4 sections. The Cardia is the entryway to the stomach, near where the stomach and esophagus meet. The Fundus is the dome shaped region located above and to the left of where the stomach and esophagus meet. The body is the largest region of the stomach and it extends to the 4th section of the stomach, the pylorus. The pylorus is a funnel shaped region that connects the stomach to the duodenum of the small intestine. The inner lining of the stomach has a rough appearance made by gastric folds. These gastric folds have gastric pits which contain gastric glands. These glands secrete most of the gastric juice released in the stomach and this juice is a mucous fluid that contains mainly digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid. There are 5 types of secretory cells that are located in the gastric epithelium. Surface mucous cells line the inner stomach and extend into the gastric pits and they secrete an alkaline fluid containing mucin that helps protect the stomach lining from exposure to the high acidity of gastric juices and gastric enzymes. Mucous neck cells are located deeper than the surface cells and they secrete an acidic mucin and which helps to maintain acidic conditions. Parietal cells produce hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor binds to vitamin B12 molecules and protects them from digestive juices until they reach the small intestine. Hydrochloric acid is not actually produced in the cells, as it forms form positive hydrogen ions and negative chlorine ions secreted from the cells. Hydrochloric acid is responsible for the low pH level in the stomach. Hcl is important in enzyme activation, unfolding certain proteins and it also protects against many microorganisms. Chief cells produce pepsinogen, which is the precursor to the enzyme pepsin. Pepsin is activated by hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and it digests or breaks down proteins into smaller peptide fragments. Chief cells also produce gastric lipase which is an enzyme that aids in the digestion of fats. G cells release gastrin into blood, which stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen, ensuring that there are enough digestive enzymes when food is present in the stomach. The outer stomach wall is comprised of 3 layers of smooth muscle tissue, an oblique muscle layer, a circular muscle layer, and a longitudinal layer, with a serosa being the outermost layer. The stomach has several important functions in your body, as it serves as a food reservoir, storing food until it can be moved into the small intestine. As we have covered, it releases gastric juice, which contains enzymes that take part in the digestion of food. The stomach actually churns food, breaking it down into smaller particles and mixing them with the gastric juice. It secretes intrinsic factor, which protects vitamin B12 molecules, which are important in cell metabolism. The stomach absorbs some alcohol, aspirin, and some short chain fatty acids. And the stomach produces gastrin to help regulate digestive functions.
05-Science


2D IS Unit 8 Section 8.8 Part B & C
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 1
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 2
Free


2021 Chem Final Exam - Explanation of Section A ( MC) Part 3
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.2 Observing ox eye cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.3 Observing onion skin cells with a microscope
Free


(New) Experiment 4.1 Using a microscope
Free


F1 IS 6.6 C Floating and sinking
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 B Test of Gas (Part 2)
Free


F2 IS 7.1 A & C Air & Application of gas
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household Electricity (Part 2)
Free


F2 IS 8.7 Household electricity (Part 1)
Free


F1 IS 5.3C Radiation (Part 2)
Free


F1 IS 5.3C Radiation (Part 1)
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section C Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section C Part 1
Free


F1 IS 5.3A Convection (Part 2)
Free


F1 IS 5.3A Convection (Part 1)
Free


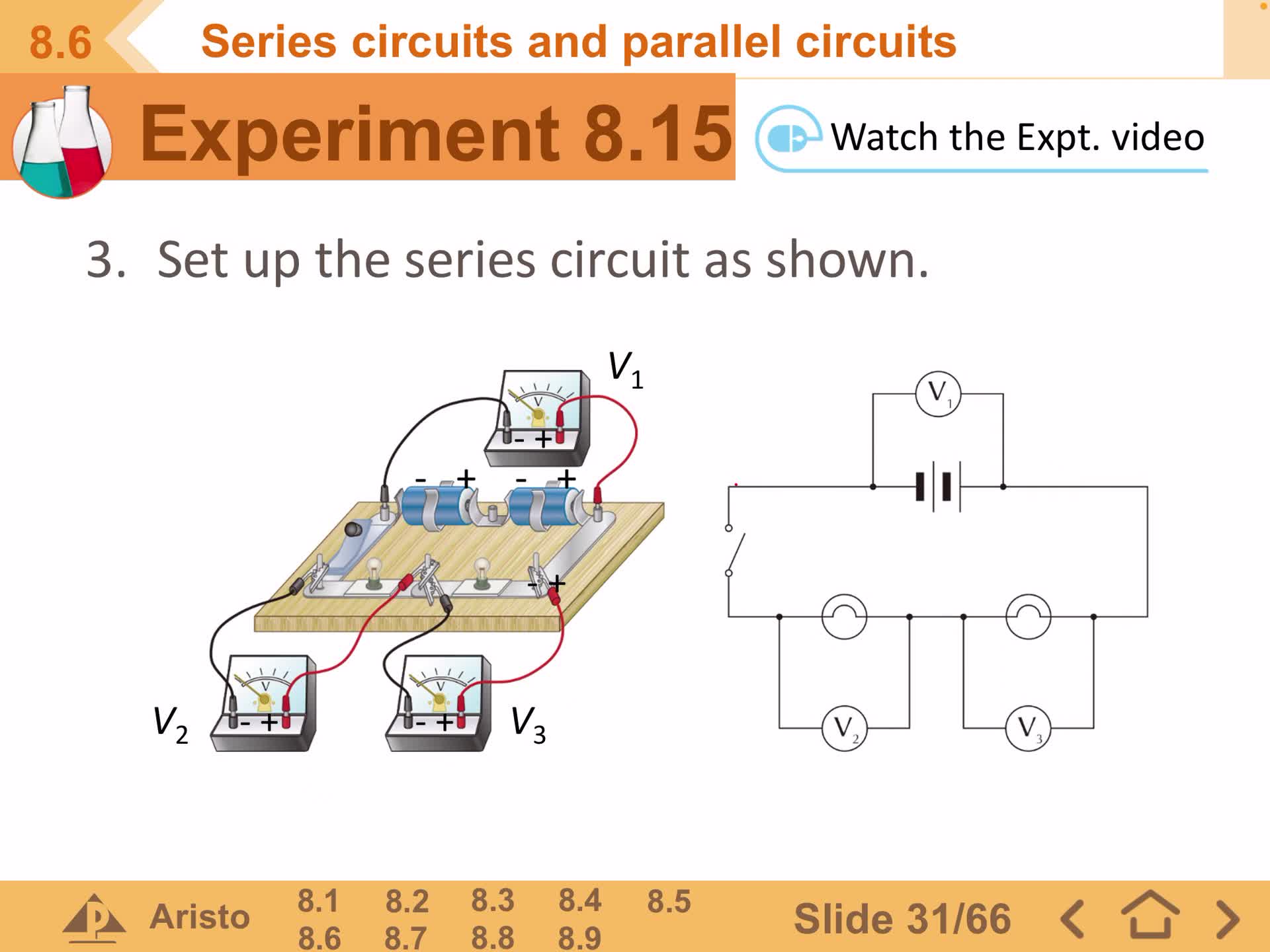
F2 IS 8.6 Series circuit and parallel circuit(part 3)
Free


F2 IS 8.6 Series circuit and parallel circuit(part 2)
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section B Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section B Part 1
Free


(NEW) Experiment 5.10 Emission of radiation from different surfaces
Free


(NEW) Experiment 5.9 Absorption of radiation by different surfaces
Free


F2 IS 8.6 Series circuit and parallel circuit(part 1)
Free


F1 IS 5.3A conduction (Part 3)
Free


F1 IS 5.3A conduction (Part 2)
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section A Part 3
Free


F2 IS 5.3A Conduction of heat (Part 1)
Free


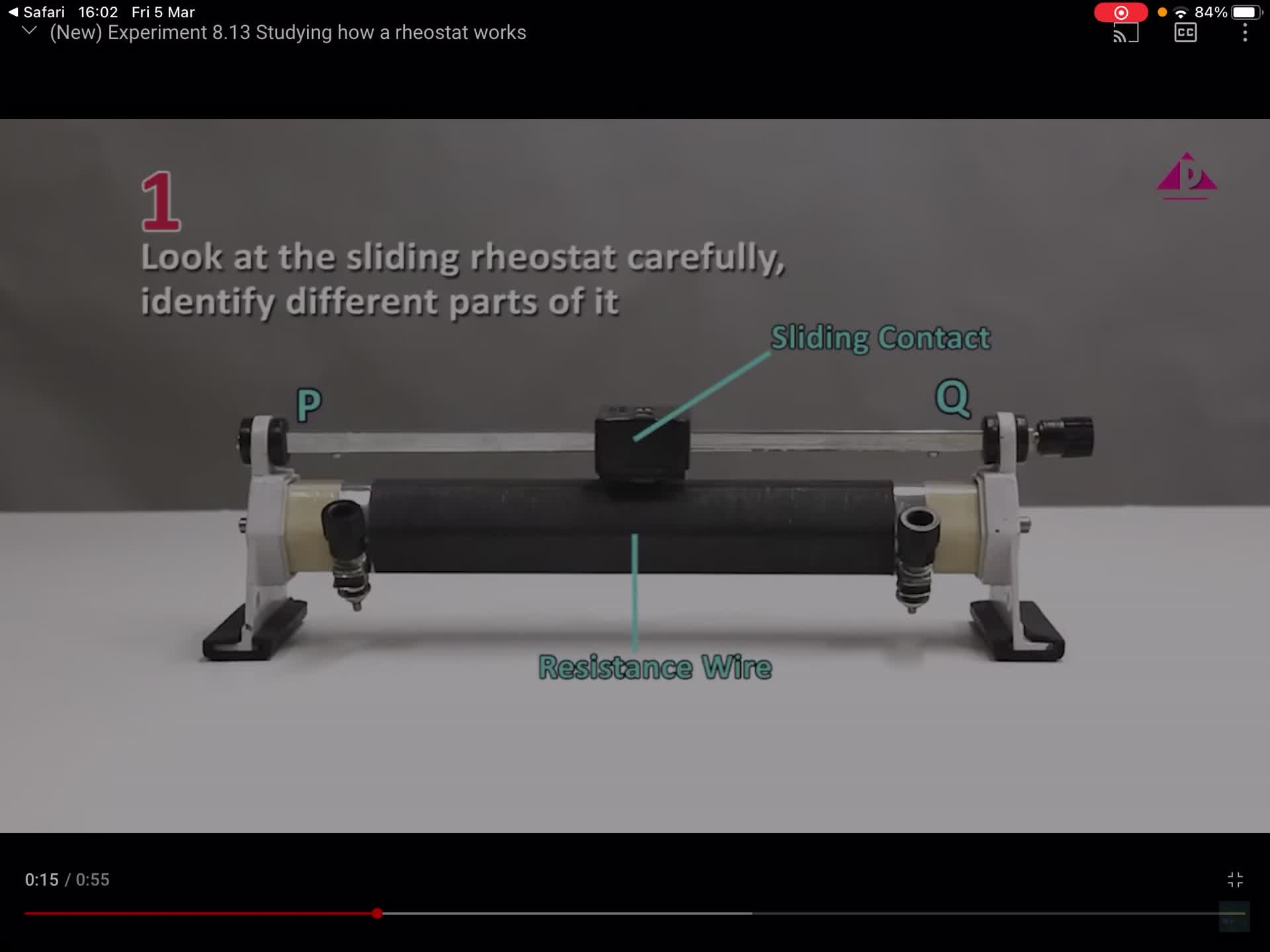
F2 IS 8.5 C Resistor & Rheostat
Free


F2 IS 8.5 C Factors affecting the resistance
Free


(NEW) Experiment 5.7 Studying the conduction of heat in a liquid and a gas
Free


(NEW) Experiment 5.5 Comparing the rate of conduction of heat in metals and non-metals
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section A Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.3 Section A Part 1
Free


F2 IS 8.5B Resistance & Current
Free


F2 IS 8.5 Resistance
Free
(NEW) Experiment 5.5 Comparing the rate of conduction of heat in metals and non-metals
496 0 05-Science Free



1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.2 Section C
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.2 Section B
Free


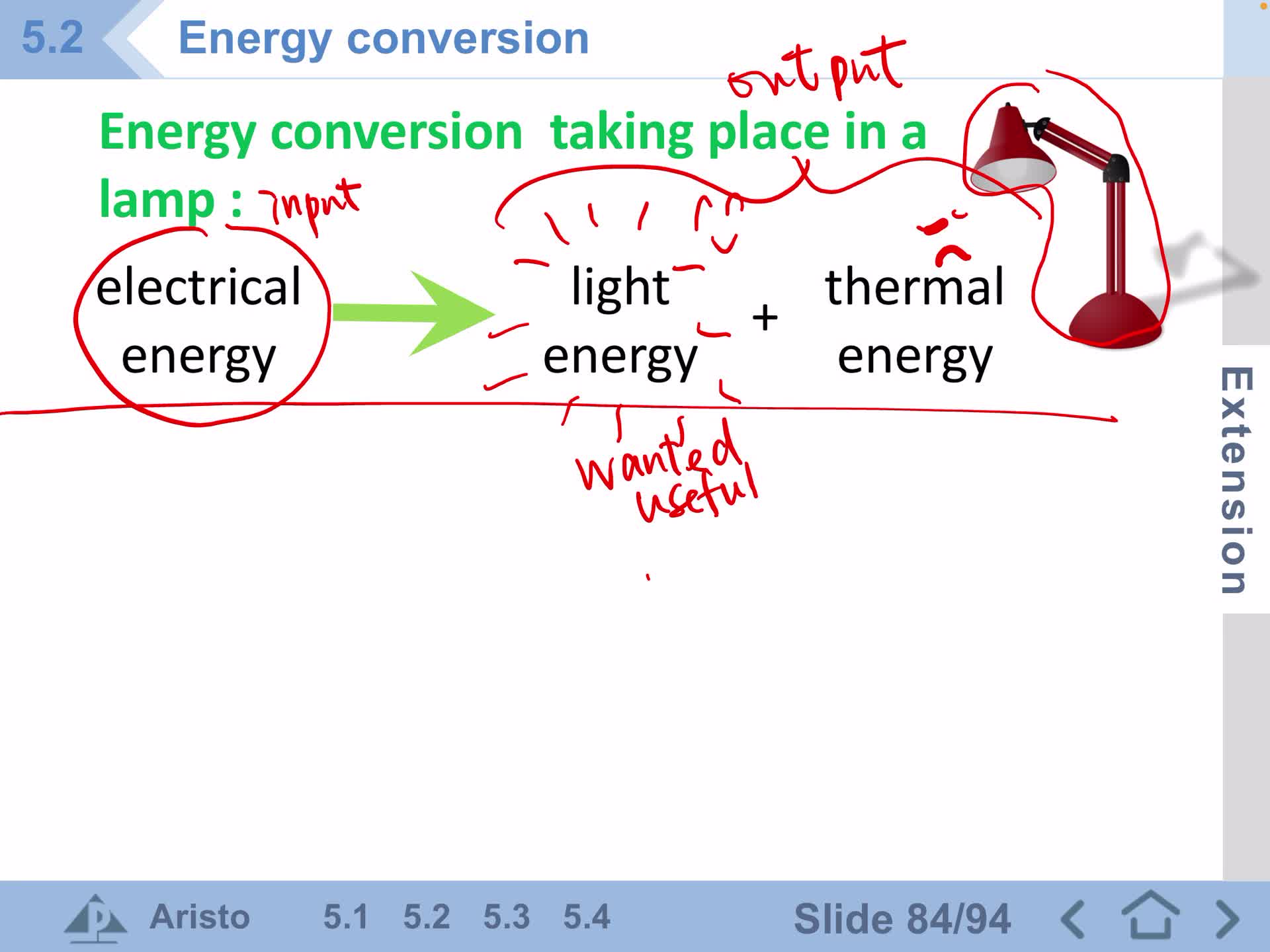
F1 IS 5.2C Efficiency of a energy converter
Free


F2 IS WB 8.4 WB Correction
Free


F1 IS 5.2A (Part 2)
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.2 Section A Part 2
Free


(NEW) Experiment 5.3 Comparing the energy stored in different stretched rubber bands
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.2 Section A Part 1
Free


F1 IS 5.2A Conversion of energy
Free


F2 IS WB 8.3 Correction
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.1 Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 5 Section 5.1 Part 1
Free


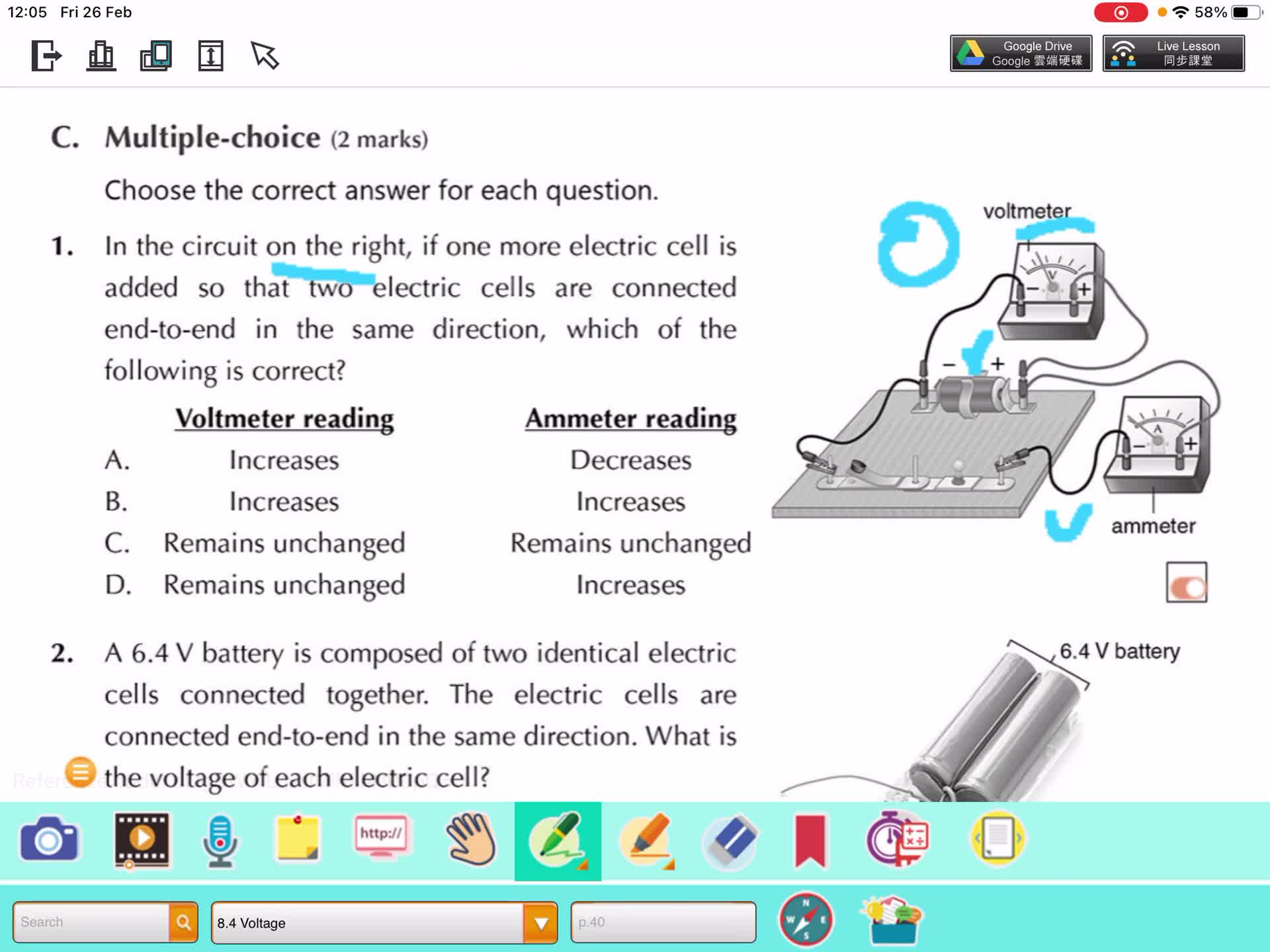
F2 IS 8.4 C Voltage & Current
Free


F2 IS 8.4 A-B Voltage & voltmeter
Free


F1 IS 5.1 Form of Energy (Part 2)
Free


F1 IS 5.1 Form of Energy (Part 1)
Free


F2 IS 8.3C Magnetic effect of current (2)
Free


F2 IS 8.3C Magnetic effect of current (1)
Free


F2 IS 8.3 C Heating effect of current
Free


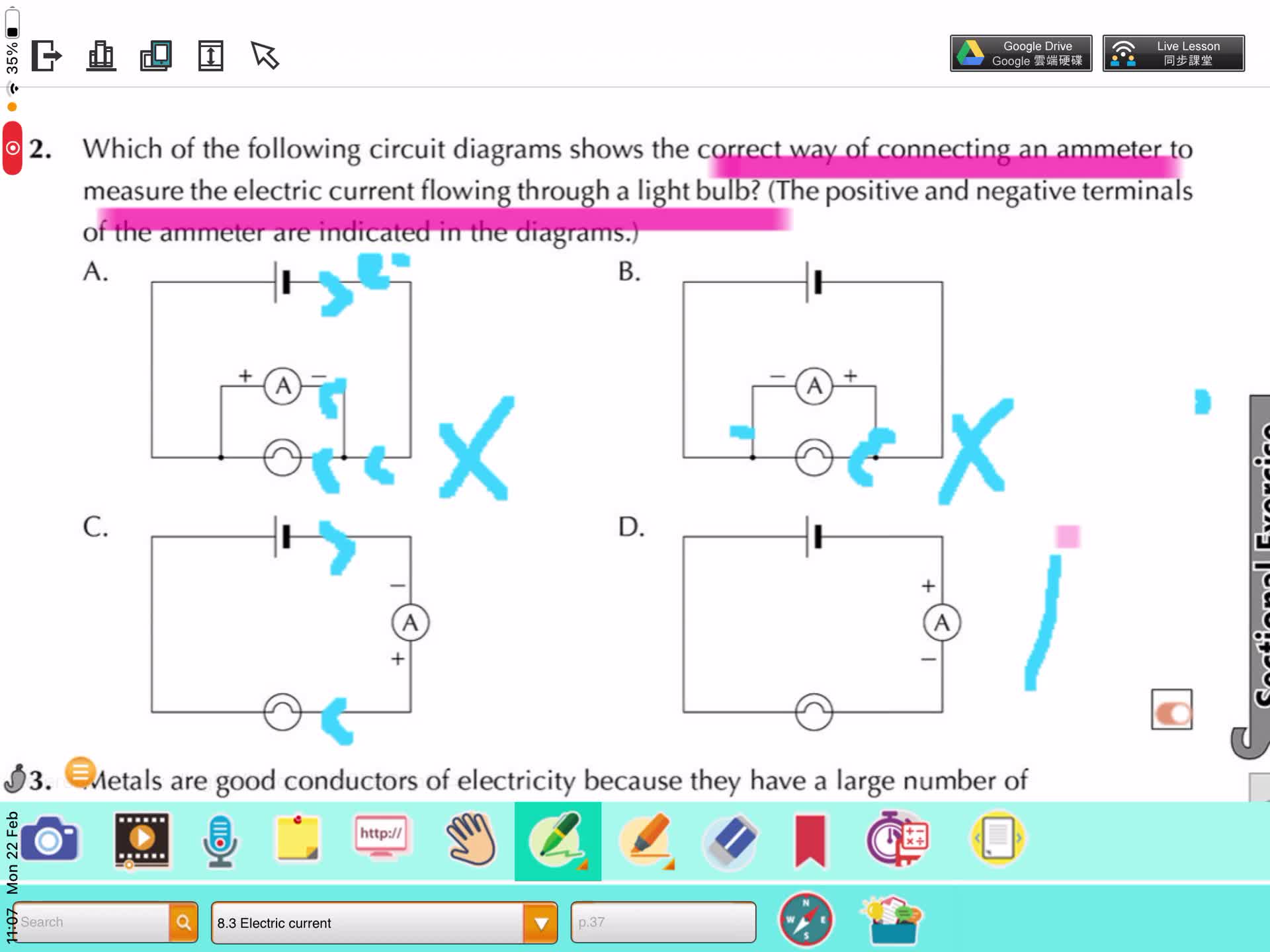
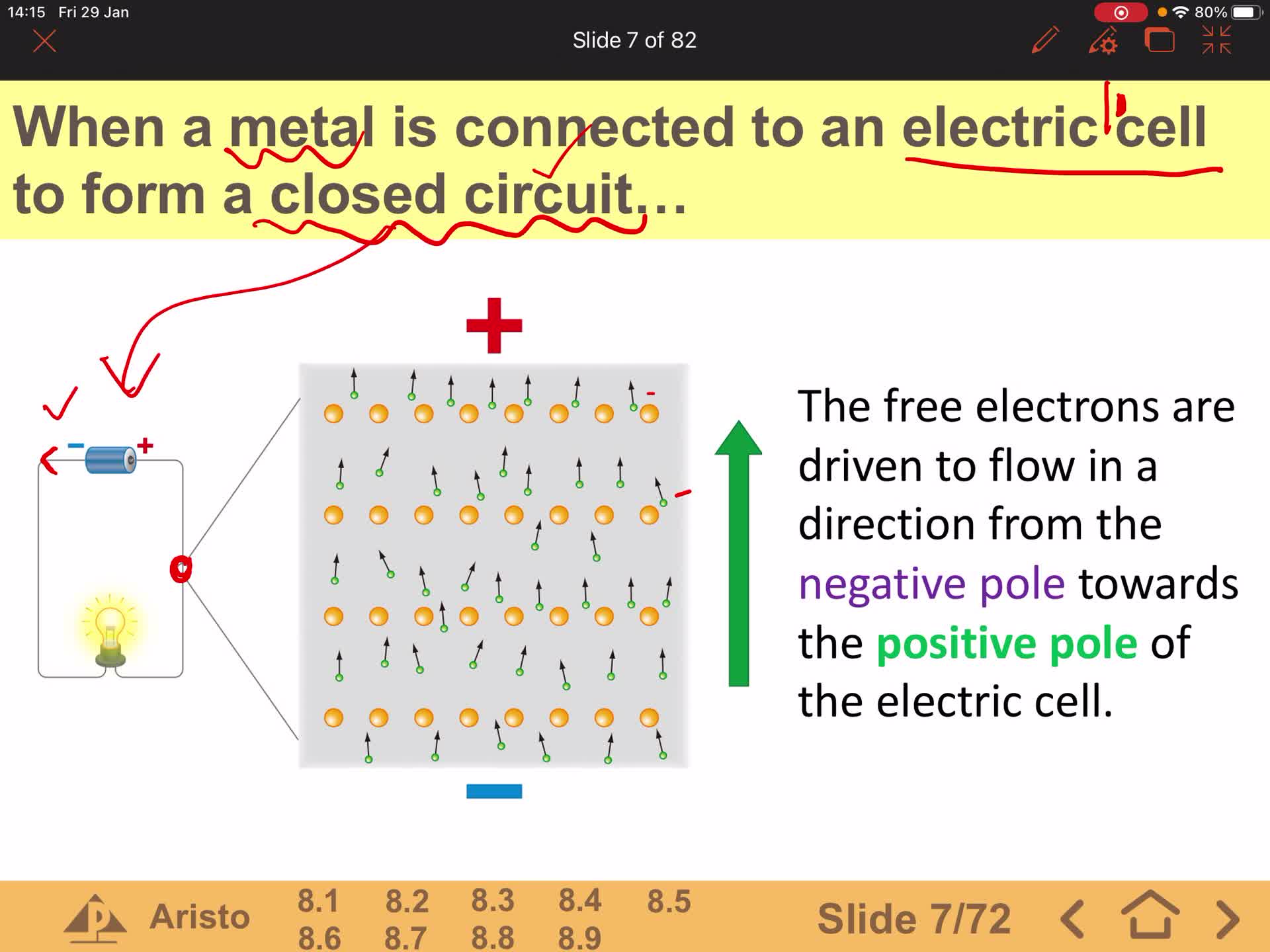
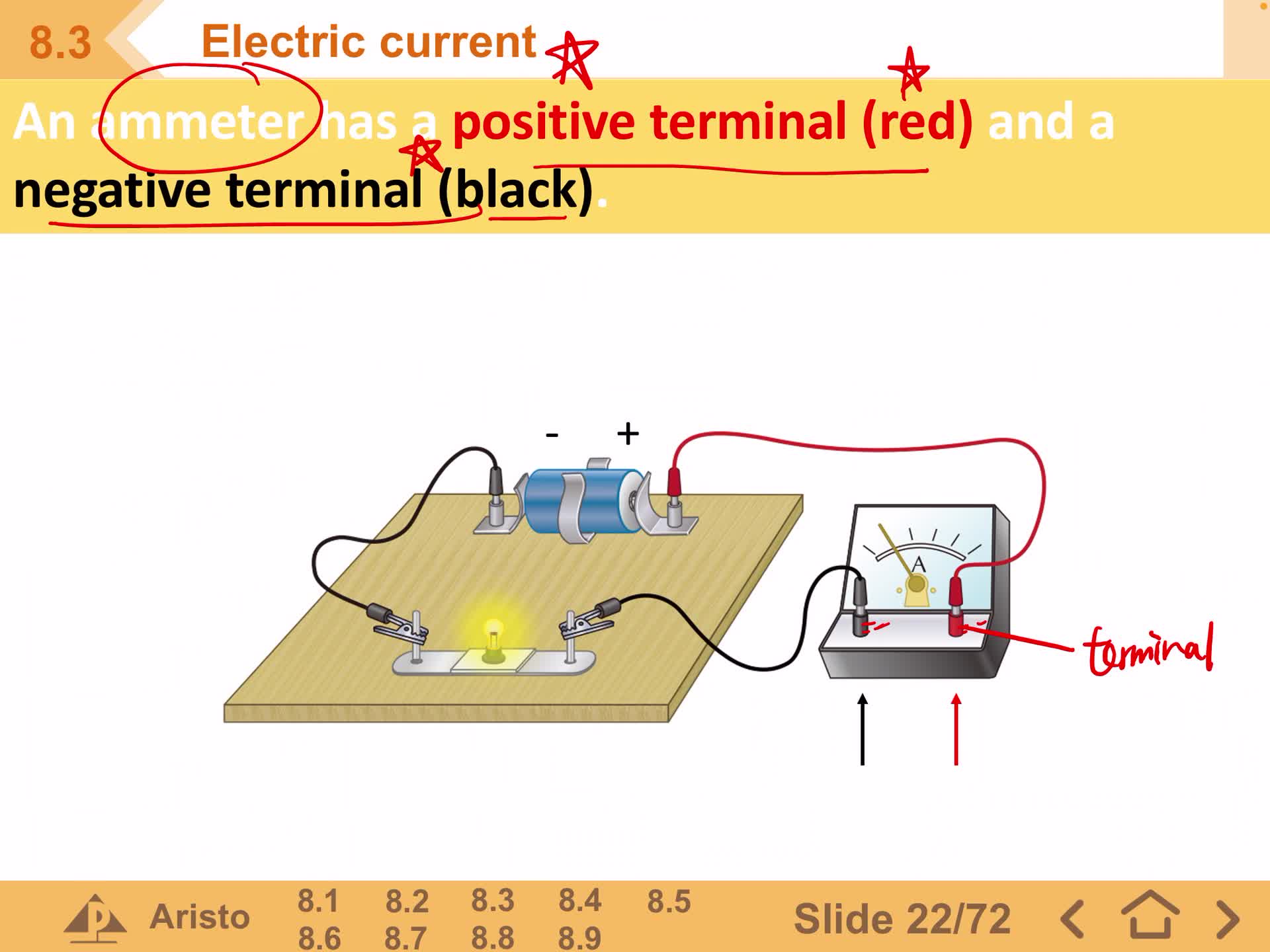
F2 IS 8.3 A Electric Current
Free
(NEW) Experiment 5.3 Comparing the energy stored in different stretched rubber bands
530 0 05-Science Free
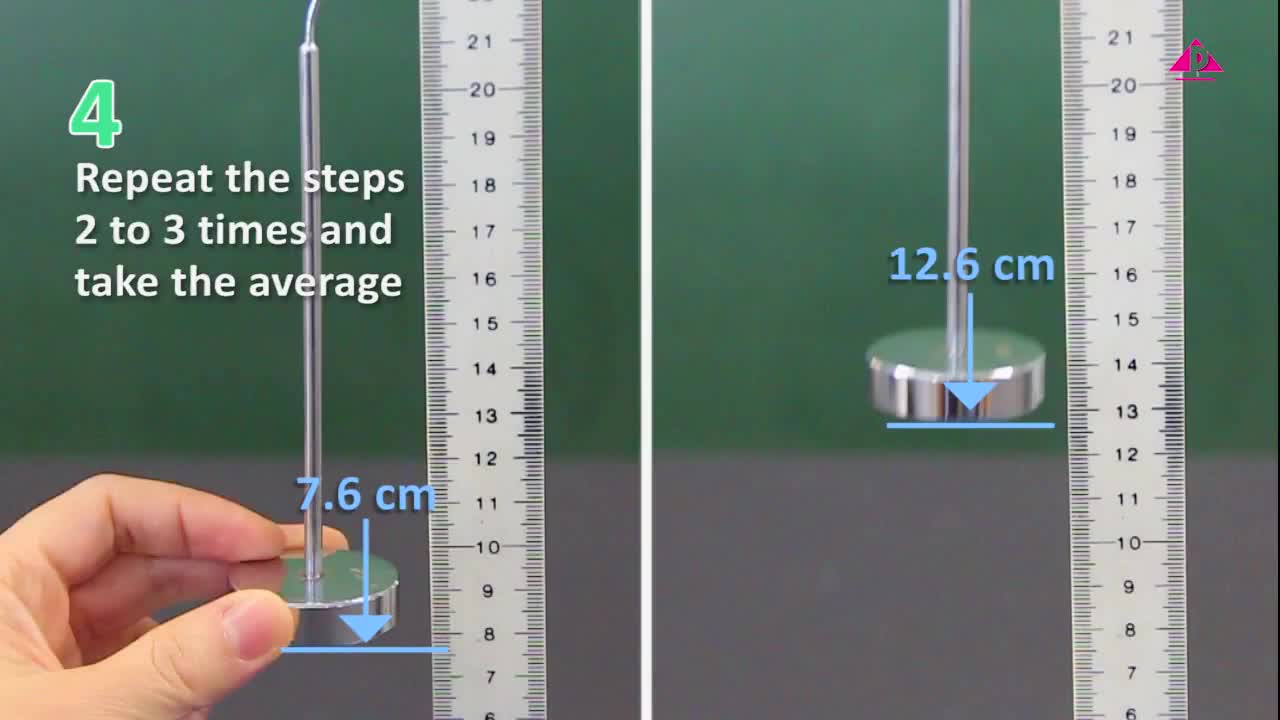


F2 IS 8.3 B Measuring of Electric Current
Free


F1 IS 3.6 保育
Free


F1 IS 3.5 多樣性減少
Free


F1 IS 3.4 生物多樣性
Free


【減塑行動。拯救海洋】海洋生物偵查庭-7 減少塑膠用品,海洋好朋友謝謝你
Free


MAN
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.6
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.5
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.4
Free


香港濕地公園@Hong Kong Wetland Park
Free


F1 IS Ch.3 作業題解
Free


F1 IS Ch.2 作業題解
Free


F2 IS Ch.10 WB 對答案
Free


F2 IS Ch.8 WB 對答案
Free


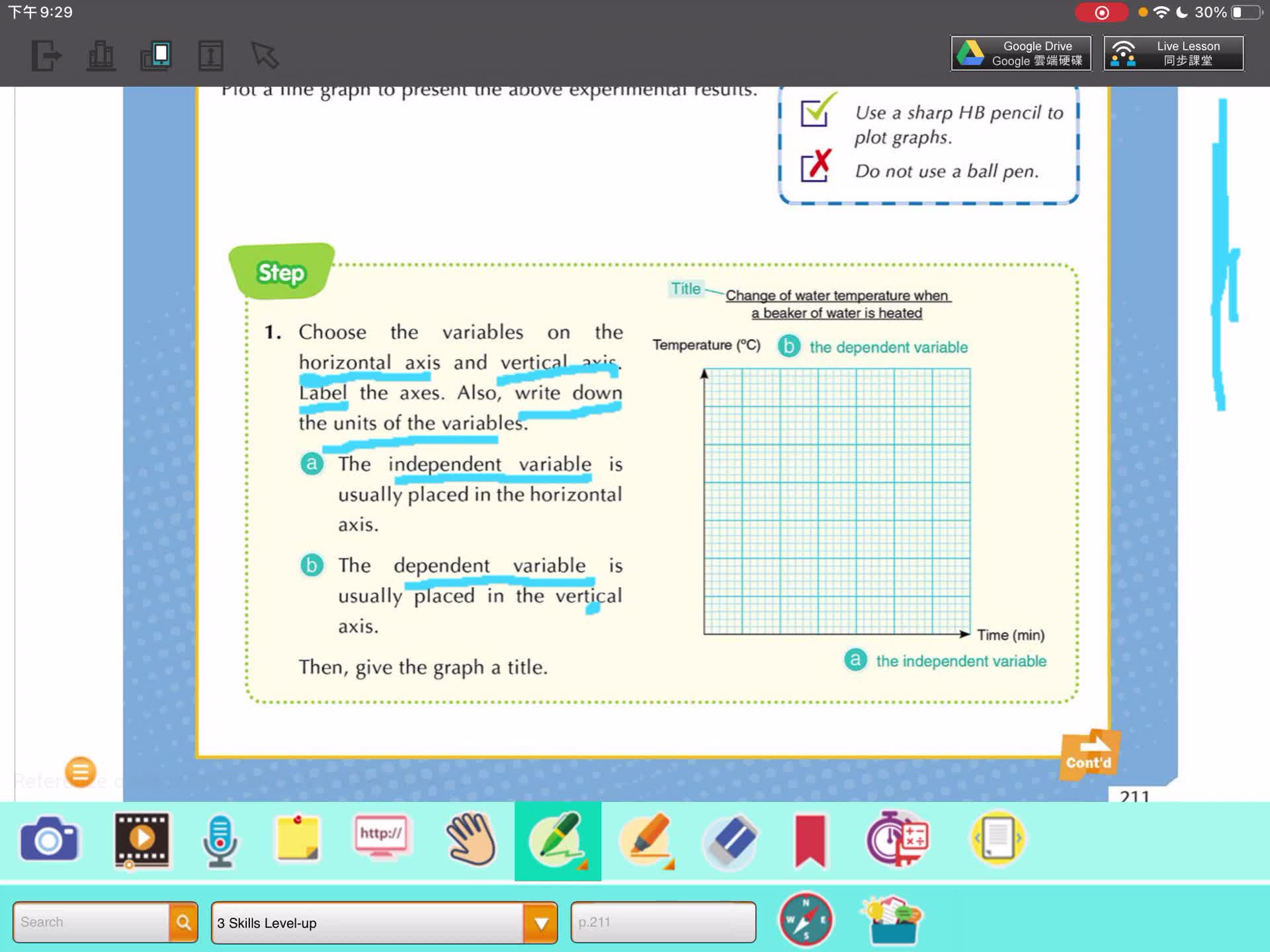
Skills of plotting graph
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.3
Free


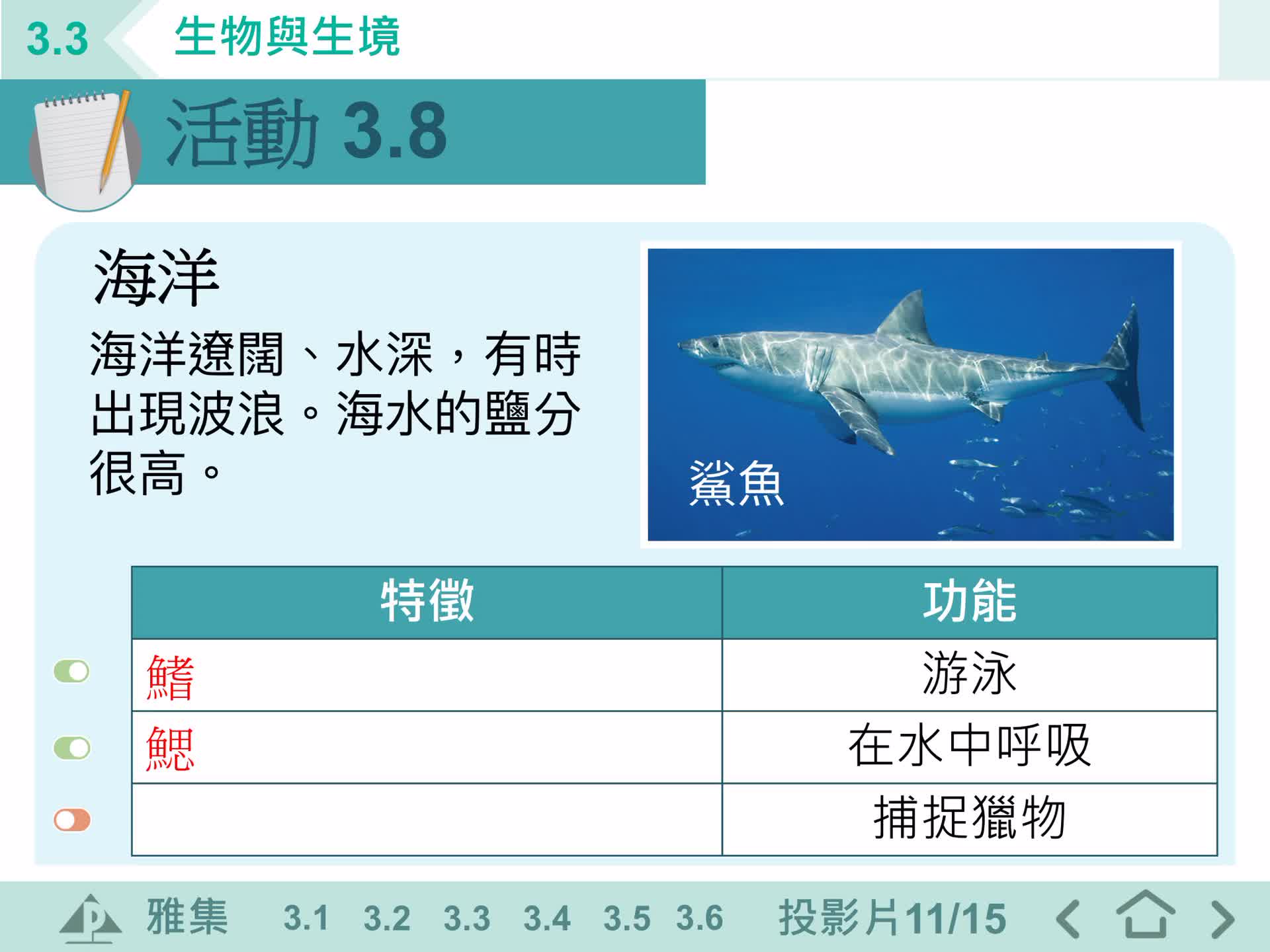
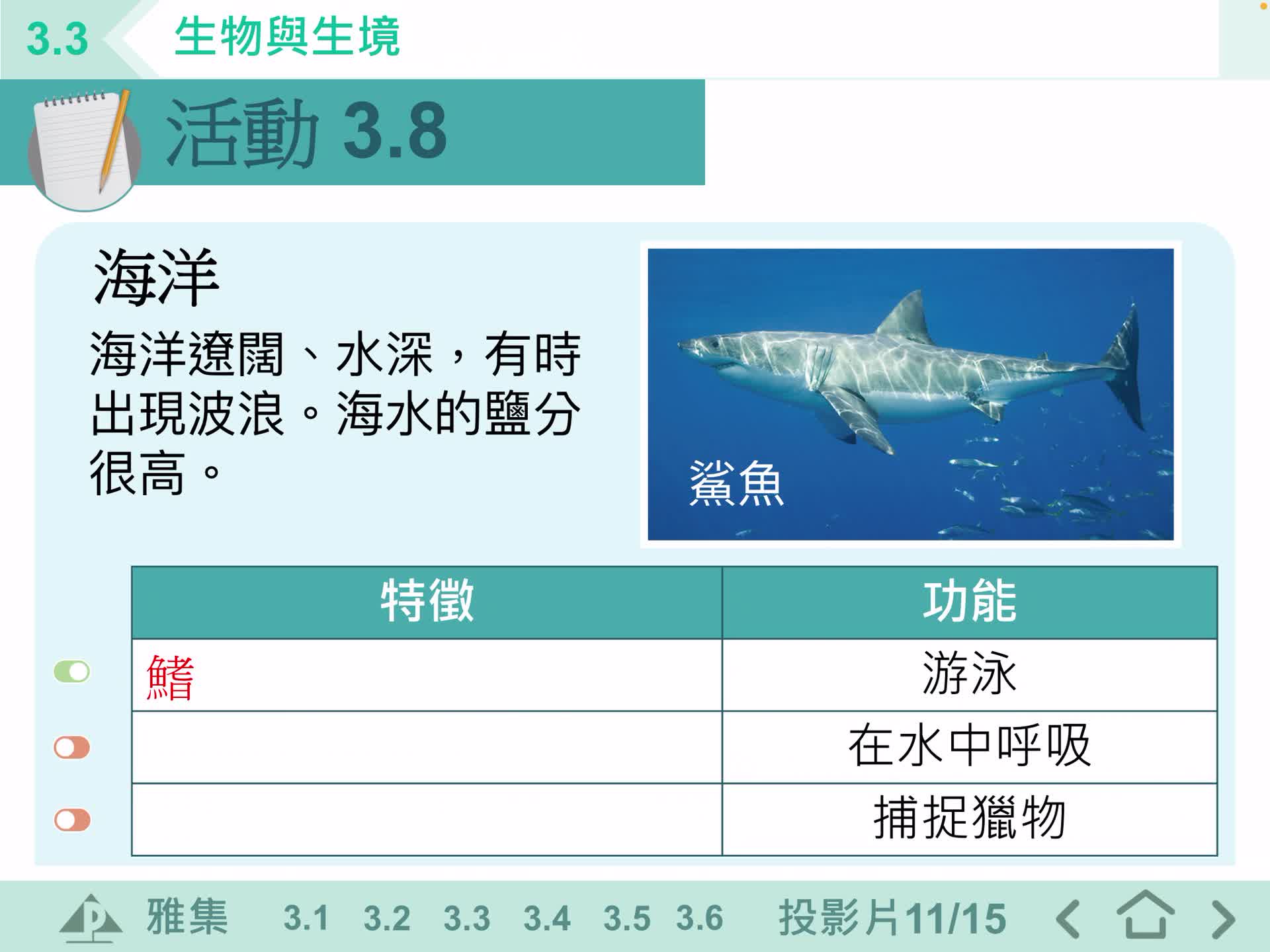
F1 IS 3.3 生物與生境
Free


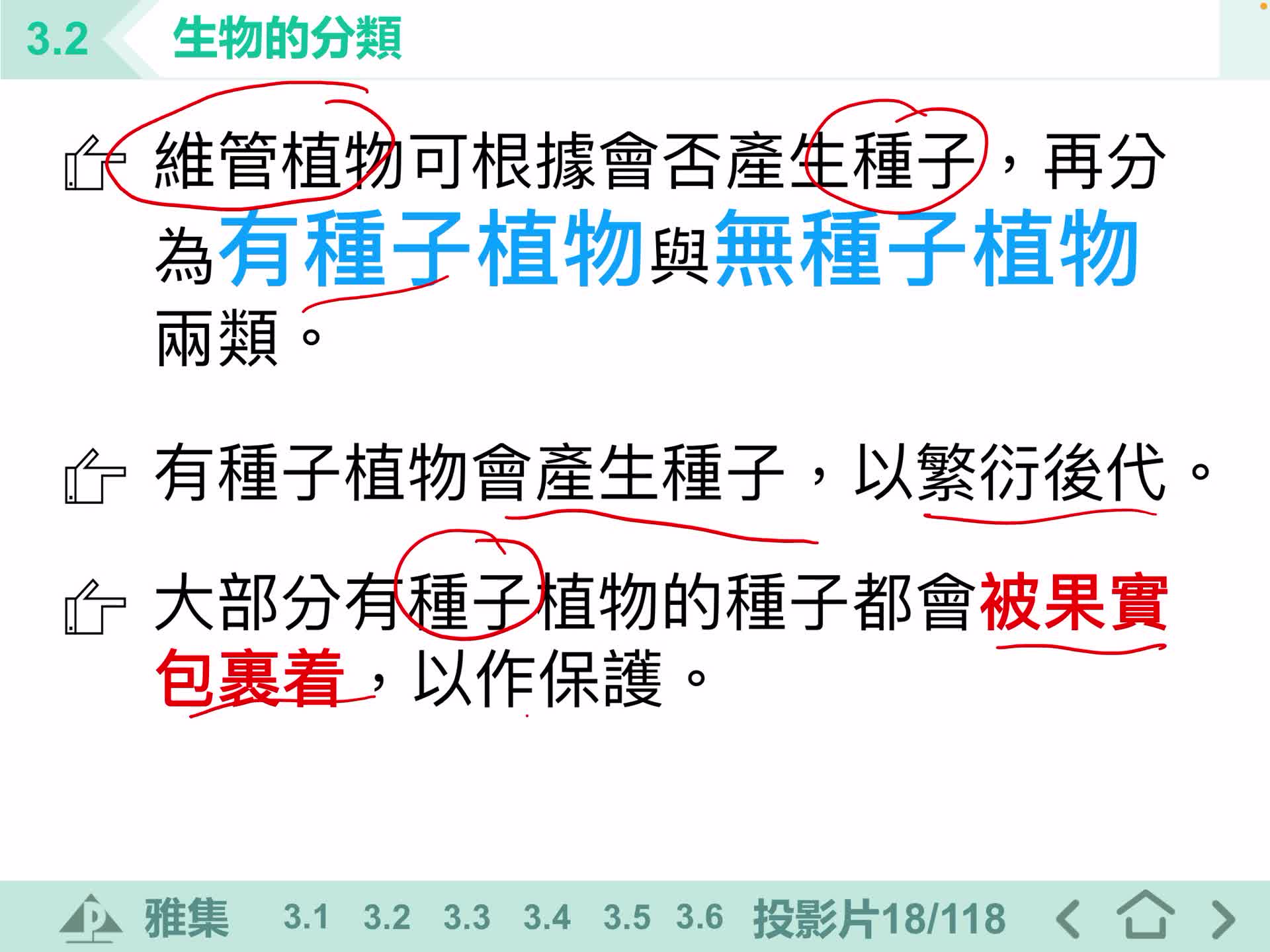
F1 IS 3.2D 植物的分類
Free


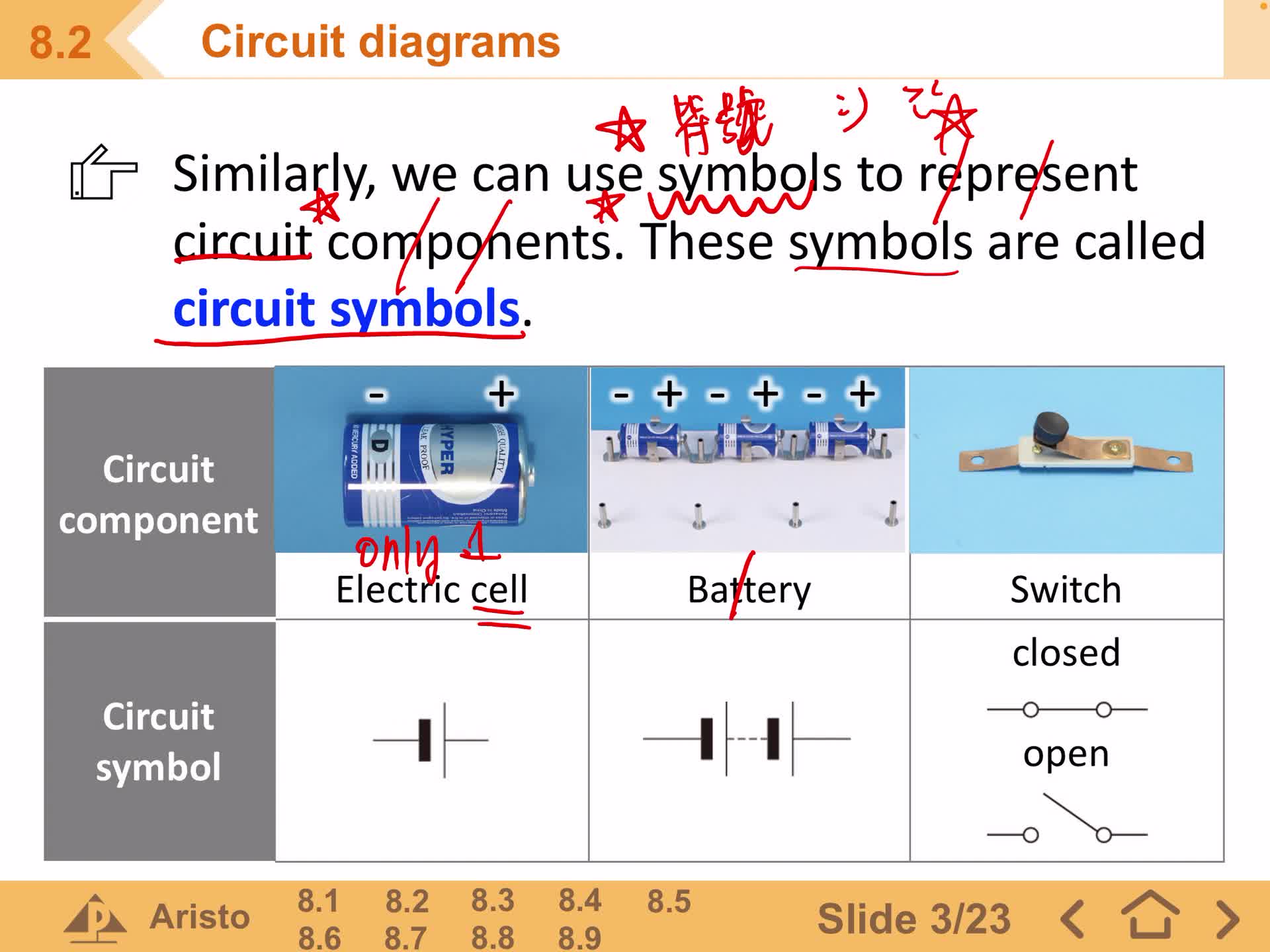
F2 IS 8.2 Circuit Diagram(2)
Free


F2 IS 8.2 Circuit Diagram(1)
Free
【減塑行動。拯救海洋】海洋生物偵查庭-7 減少塑膠用品,海洋好朋友謝謝你
510 0 05-Science Free
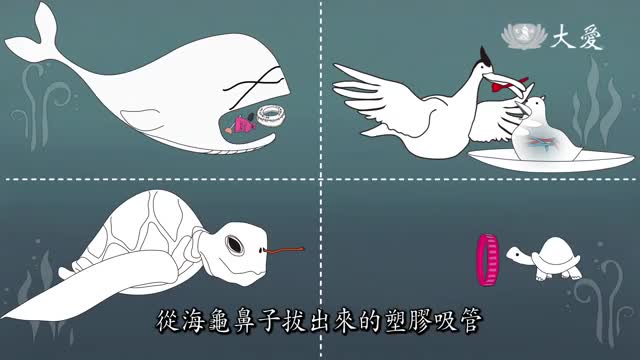
這裡是宇宙裡最美麗的星球,地球。湛藍美麗的大海,你們看是不是很美?但仔細看看海裡面是什麼?通通都是塑膠垃圾!垃圾在海面上飄,它的面積有535個臺灣大,而且還一直在增加中,很多海洋生物好朋友們都因此受害了!我是小鯨魚小梧子,減少塑膠用品我和我的海洋好朋友謝謝你!
MAN
513 0 05-Science Free

Animation created in Flash and After Effects looking at mans relationship with the natural world. Music: In the Hall of the Mountain King by Edvard Grieg. "Hall of the Mountain King" Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com) Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ https://www.facebook.com/SteveCuttsArt https://twitter.com/Steve_Cutts http://www.stevecutts.com Copyright © 2012 www.stevecutts.com
香港濕地公園@Hong Kong Wetland Park
496 0 05-Science Free

香港濕地公園@Hong Kong Wetland Park, taken with Sony HandyCam FDR-AXP55 [13 Sep 2018] #香港濕地公園


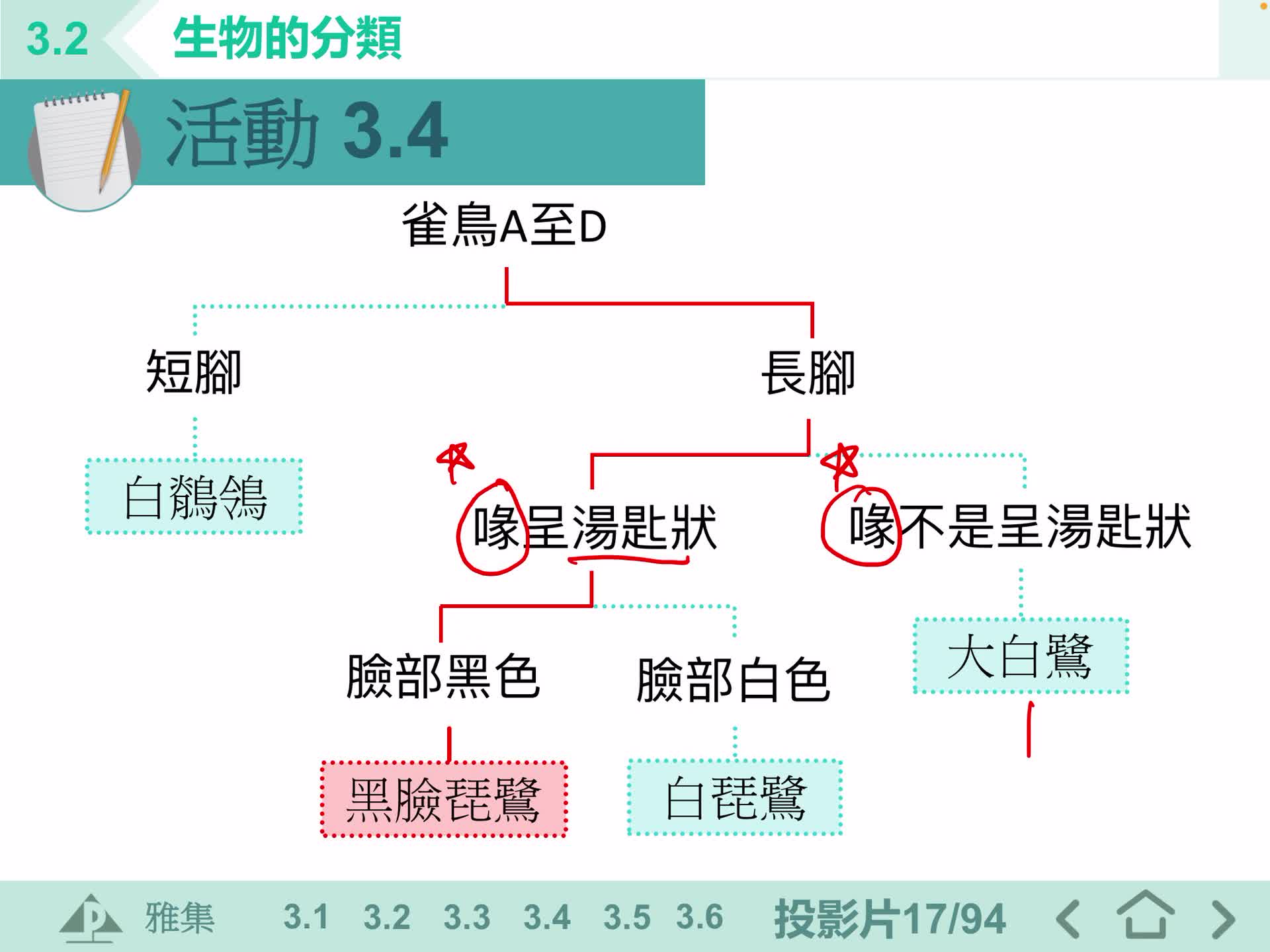
F1 IS 3.2C 脊椎動物的分類(2)
Free


F1 IS 3.2C 脊椎動物的分類(1)
Free


F1 IS 3.2A-B 生物分類及檢索表
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.2 D
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.2 C Part 2
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.2 C Part 1
Free


1A IS Unit 3 Section 3.2 A & B
Free


F1 IS 3.1
Free


F2 IS 8.1 C-D
Free


F2 IS 8.1 A-B
Free


F2 IS 10.7 E 酒精 藥物 有機溶劑
Free


F2 IS 10.7 腦的功能及錯覺
Free


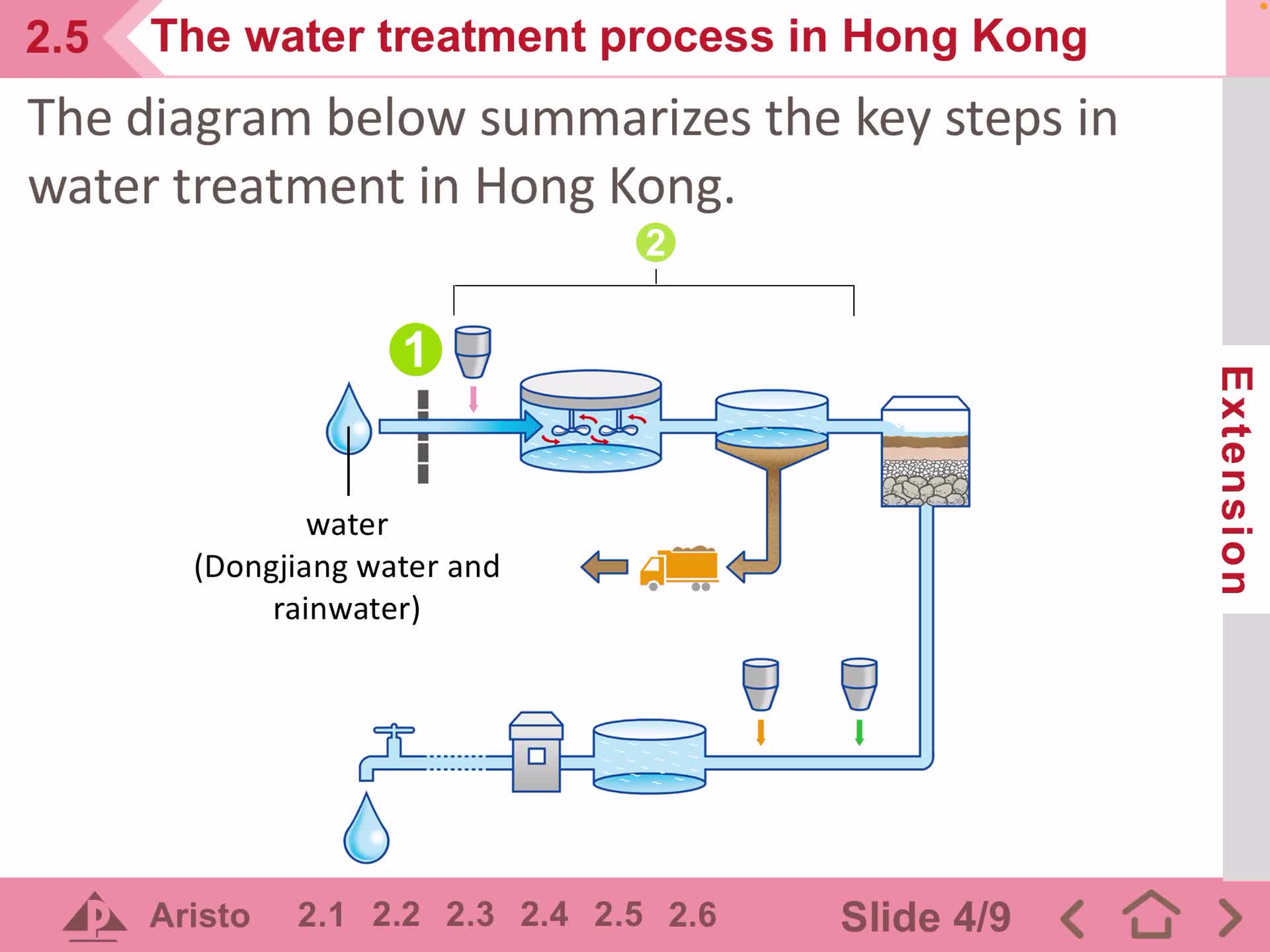
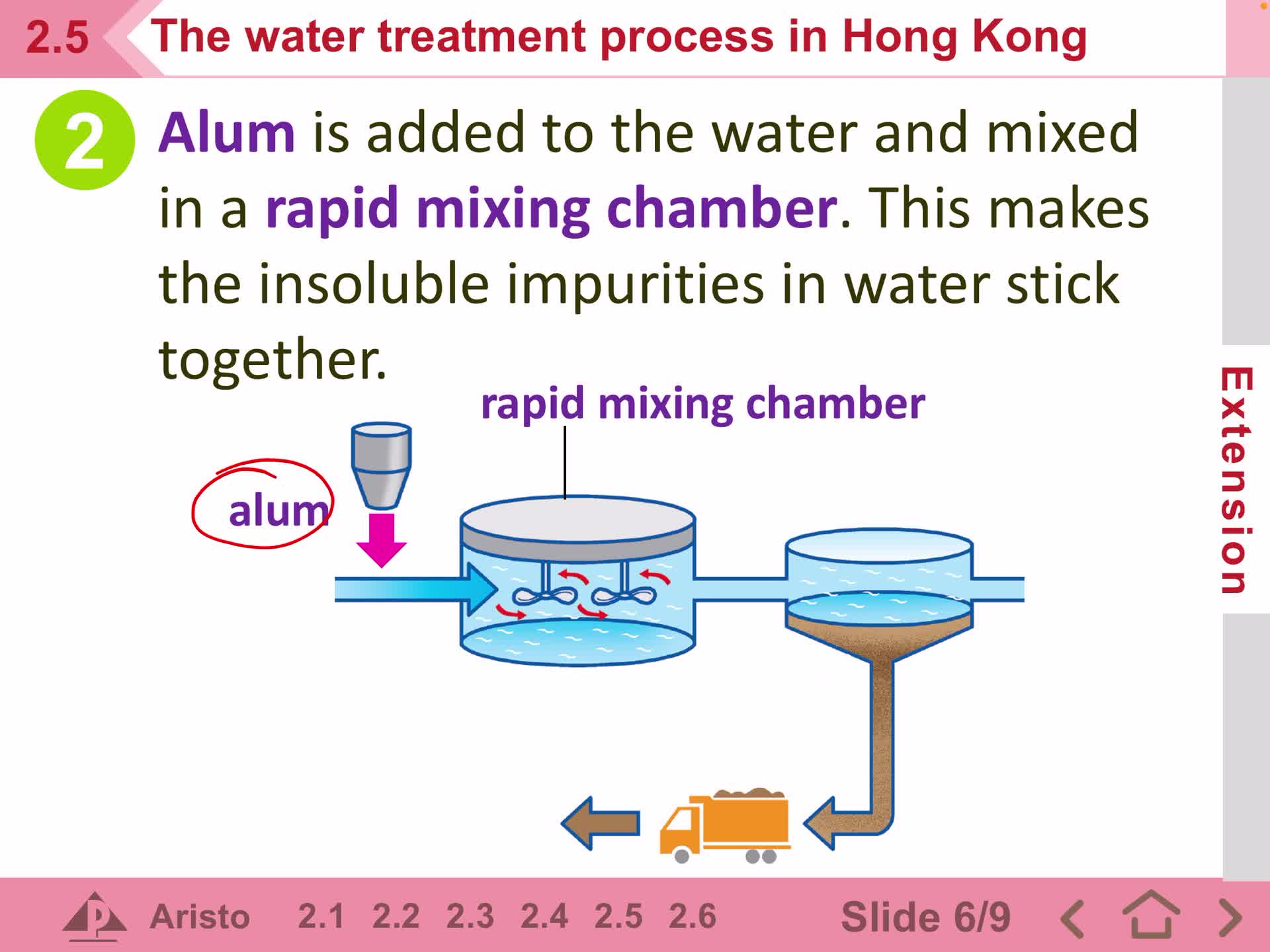
F1 IS. 2.5 Water treatment in HK - Part 3
Free


F1 IS. 2.5 Water treatment in HK - Part 2
Free


F1 IS. 2.5 Water treatment in HK - Part 1
Free


F1 IS 24 Further treatment of drinking water
Free


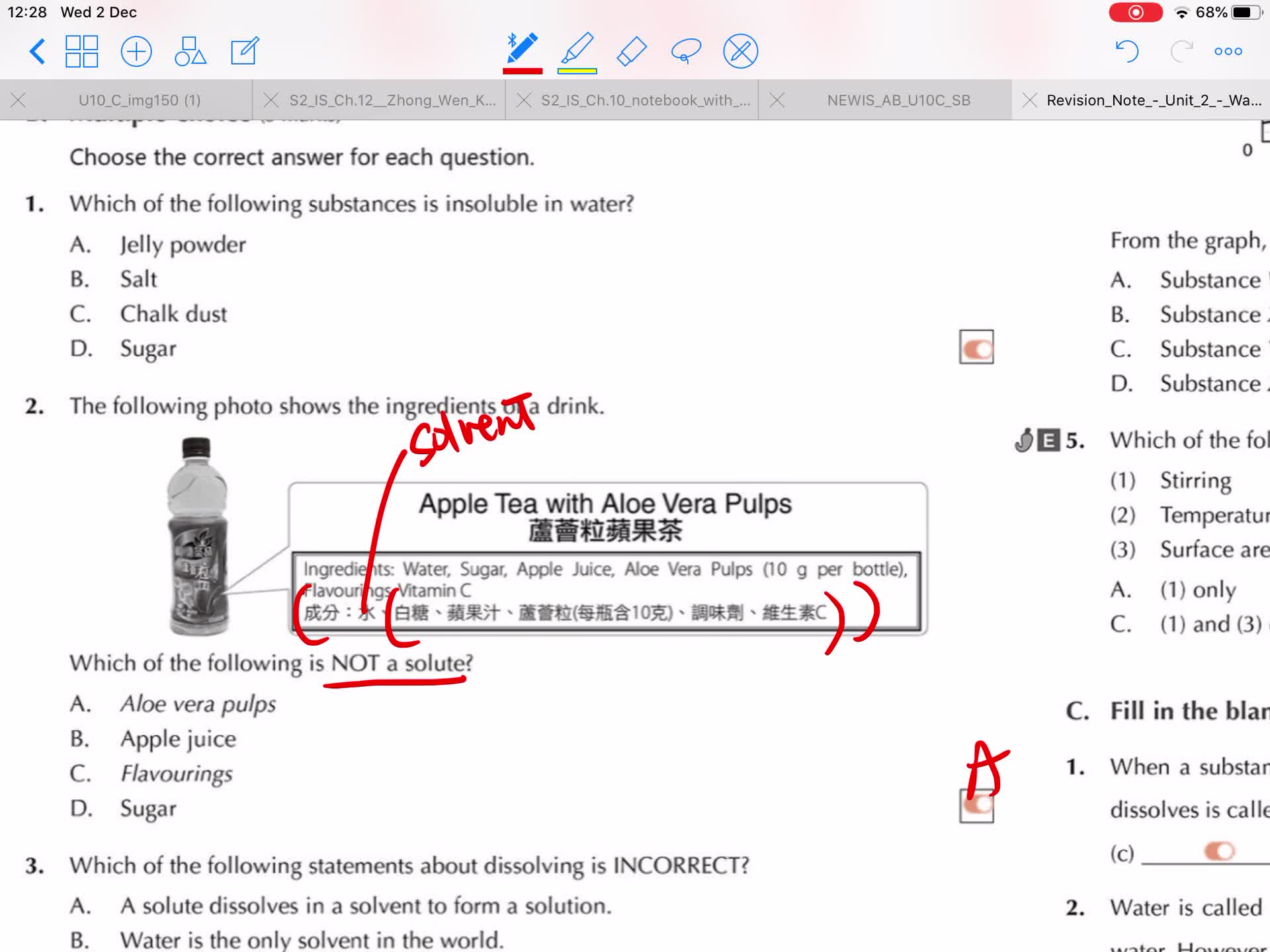
1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.5
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.4
Free


F2 IS 10.7 感覺和腦及反應時間
Free


F1 IS 2.3 Distillation
Free


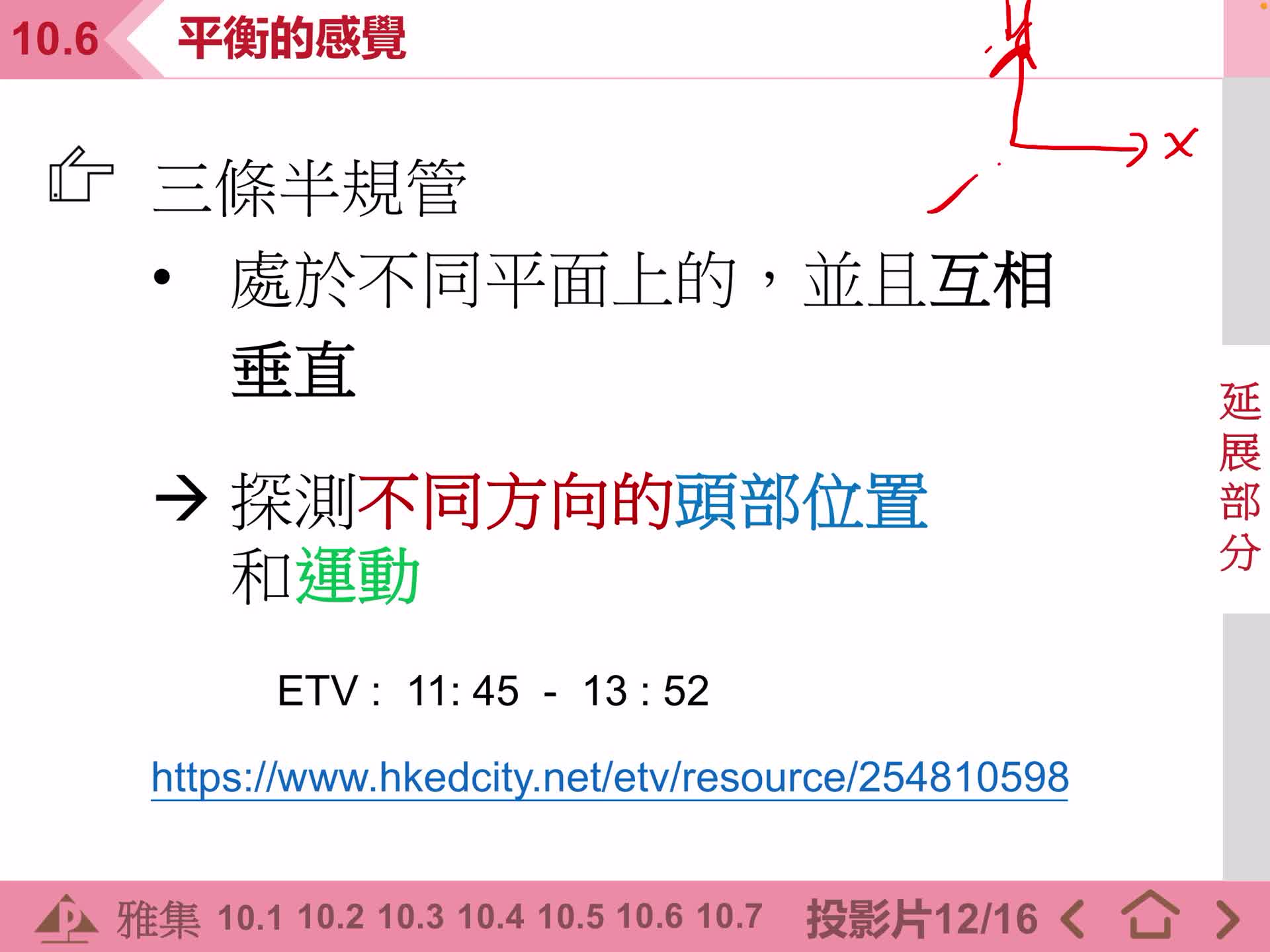
F2 IS 10.6 平衡的感覺
Free


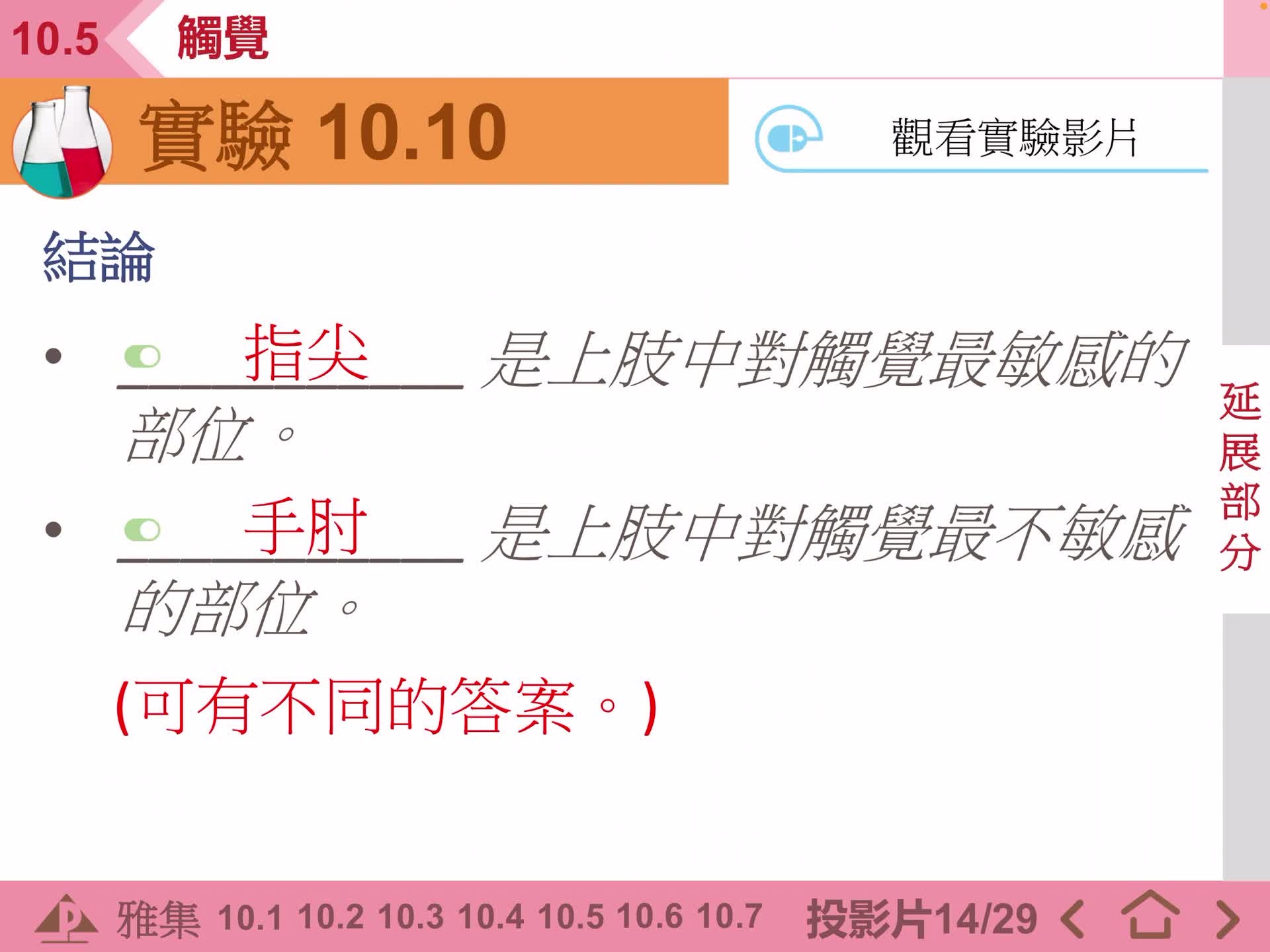
F2 IS 10.5 觸覺
Free


F1 IS 2.3 C Methods of purification
Free


F1 IS 2.3 C Methods of purification
Free


F1 IS 2.3 C Methods of purification
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.3 Part C 3
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.3 Part C 2
Free


F2 IS 10.4 味覺和嗅覺
Free


F1 IS 2.3_A & B
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.3 Part C 1
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.3 Part A-B
Free


1A IS Unit 2 Section 2.2 Part C
Free


F1 IS 2.2 Tutorials
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.13
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.12
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.11
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.10
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.9
Free


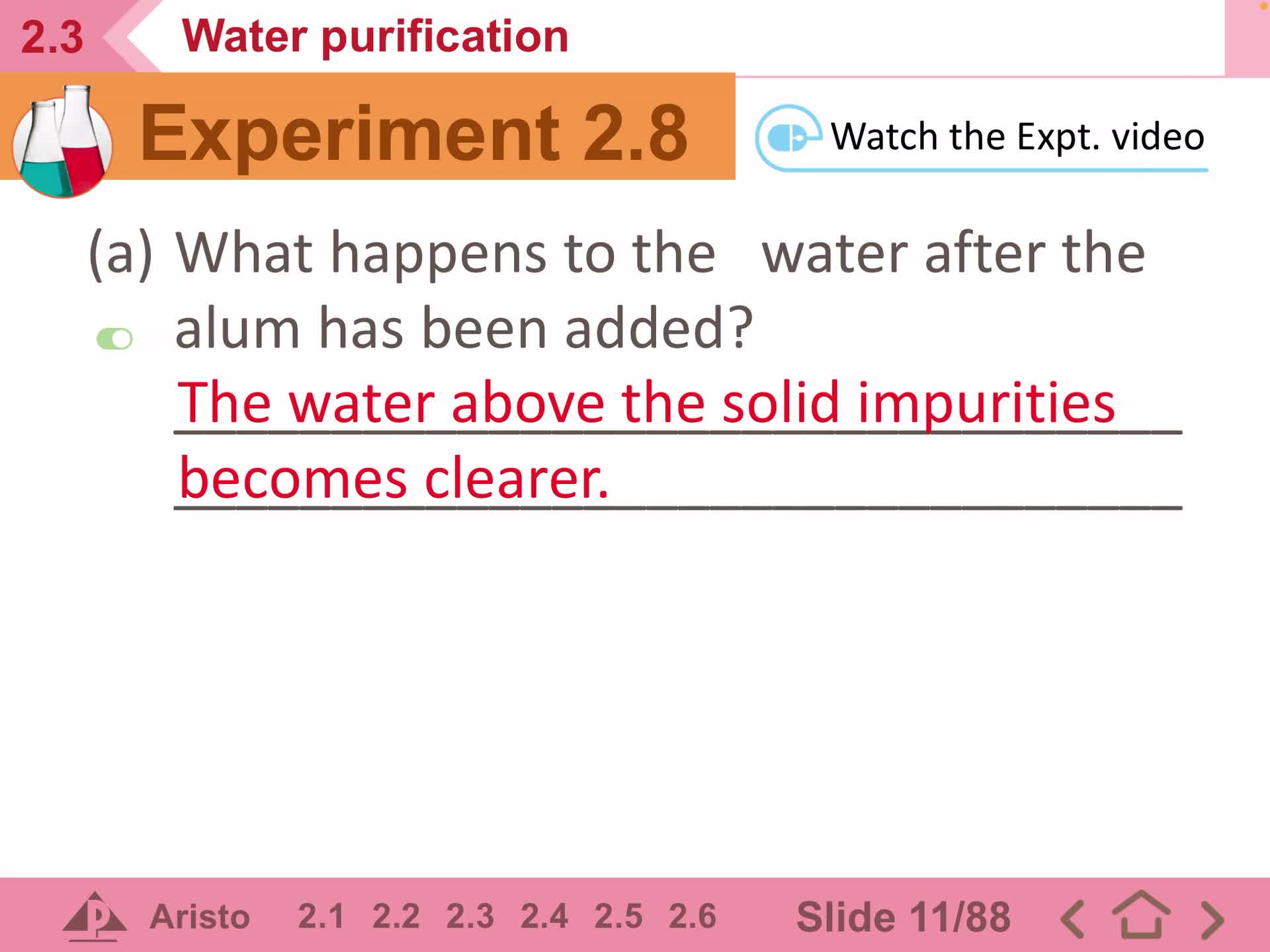
IS_S1_Expt_2.8
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.7
Free


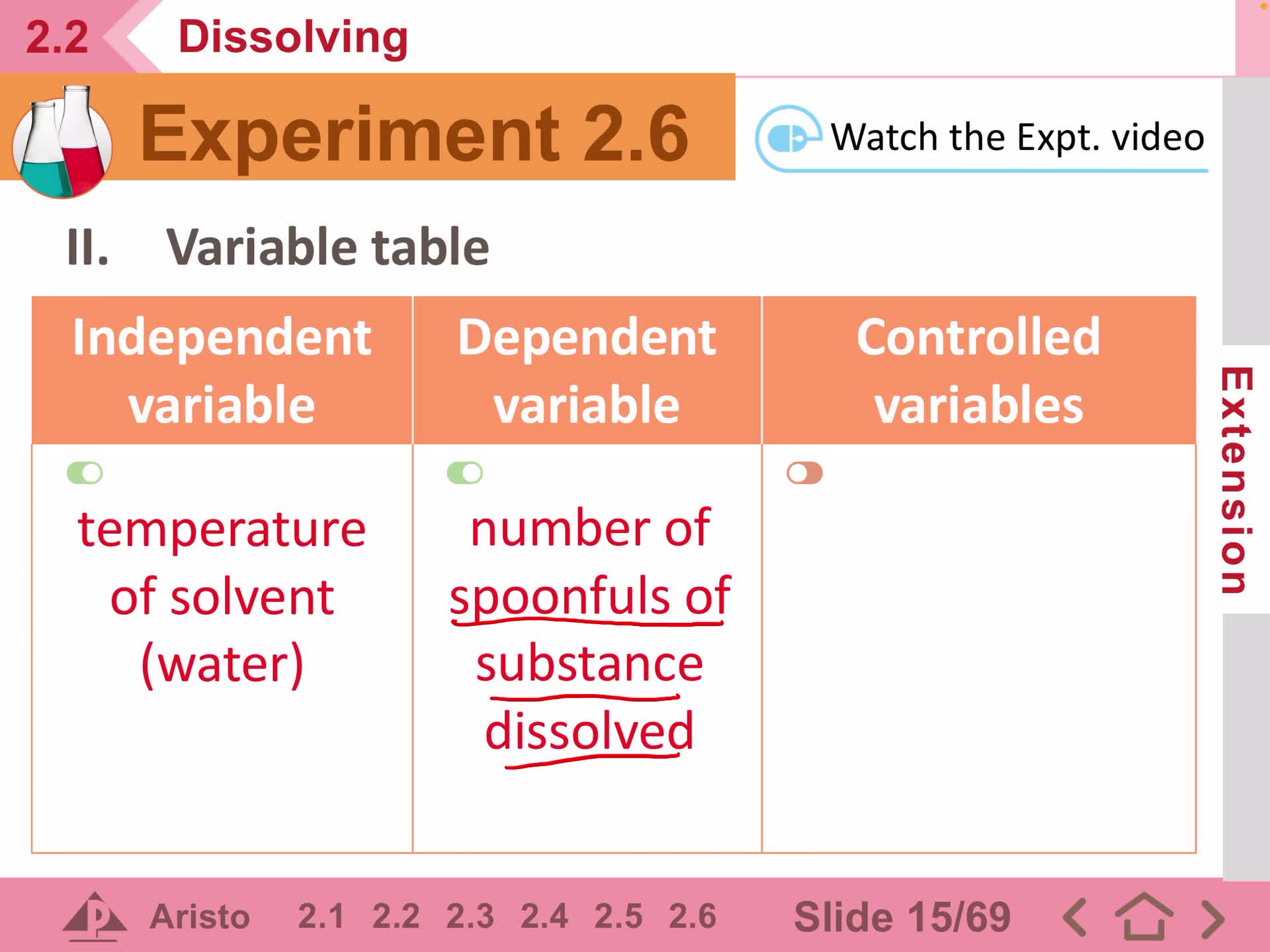
IS_S1_Expt_2.6
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.5
Free


IS_S1_Expt_2.4
Free


IS_S1_Expt_1.10
Free


IS_S1_Expt_1.9
Free


IS_S1_Expt_1.11
Free


11.3-11.4 Quiz Correction
Free


Answer of 11.3-11.4 NB, WB & WS
Free


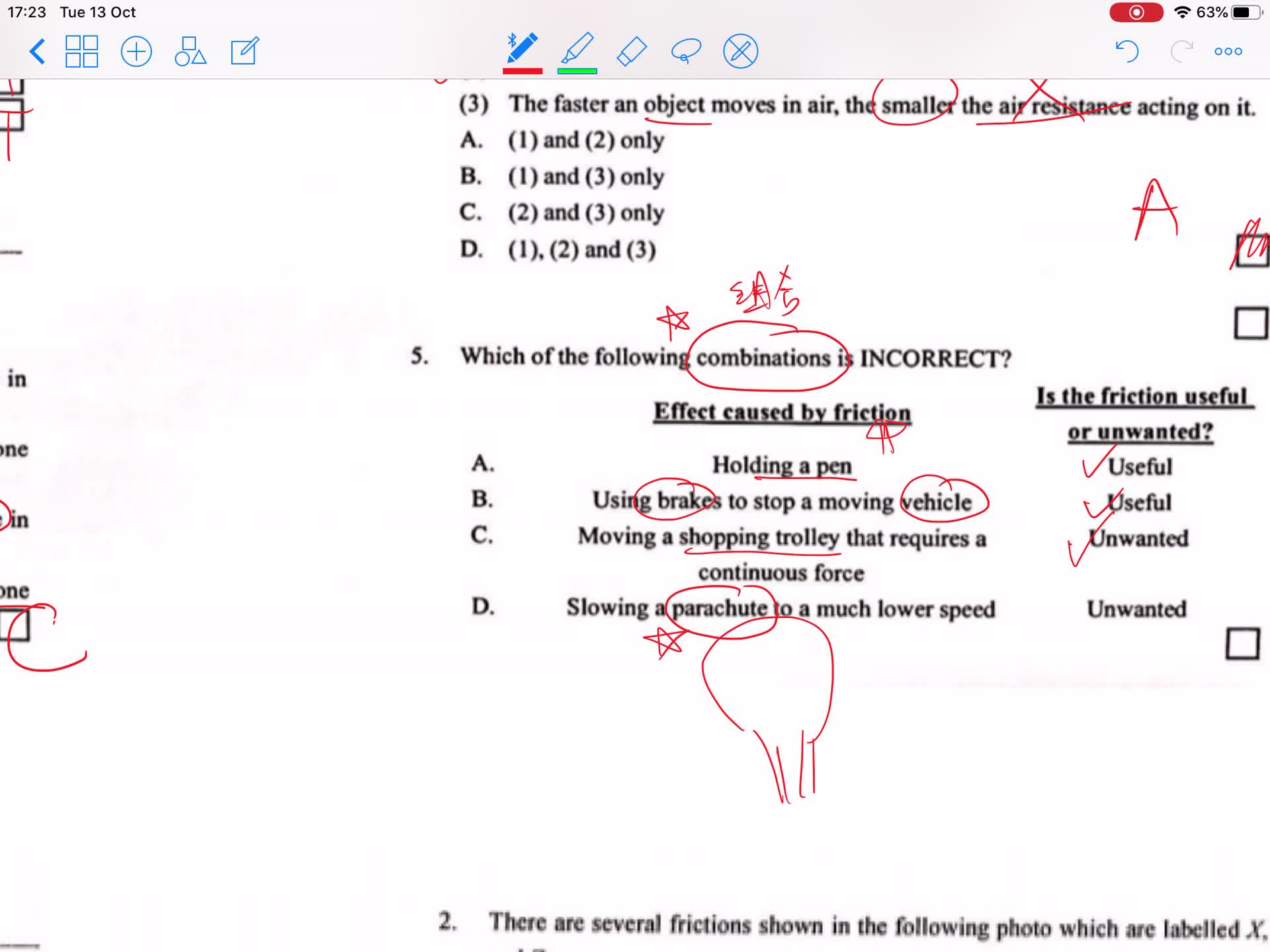
Making use of friction & air resistance


Reducing friction & Air resistance II


Reducing friction & Air resistance I


Air resistance


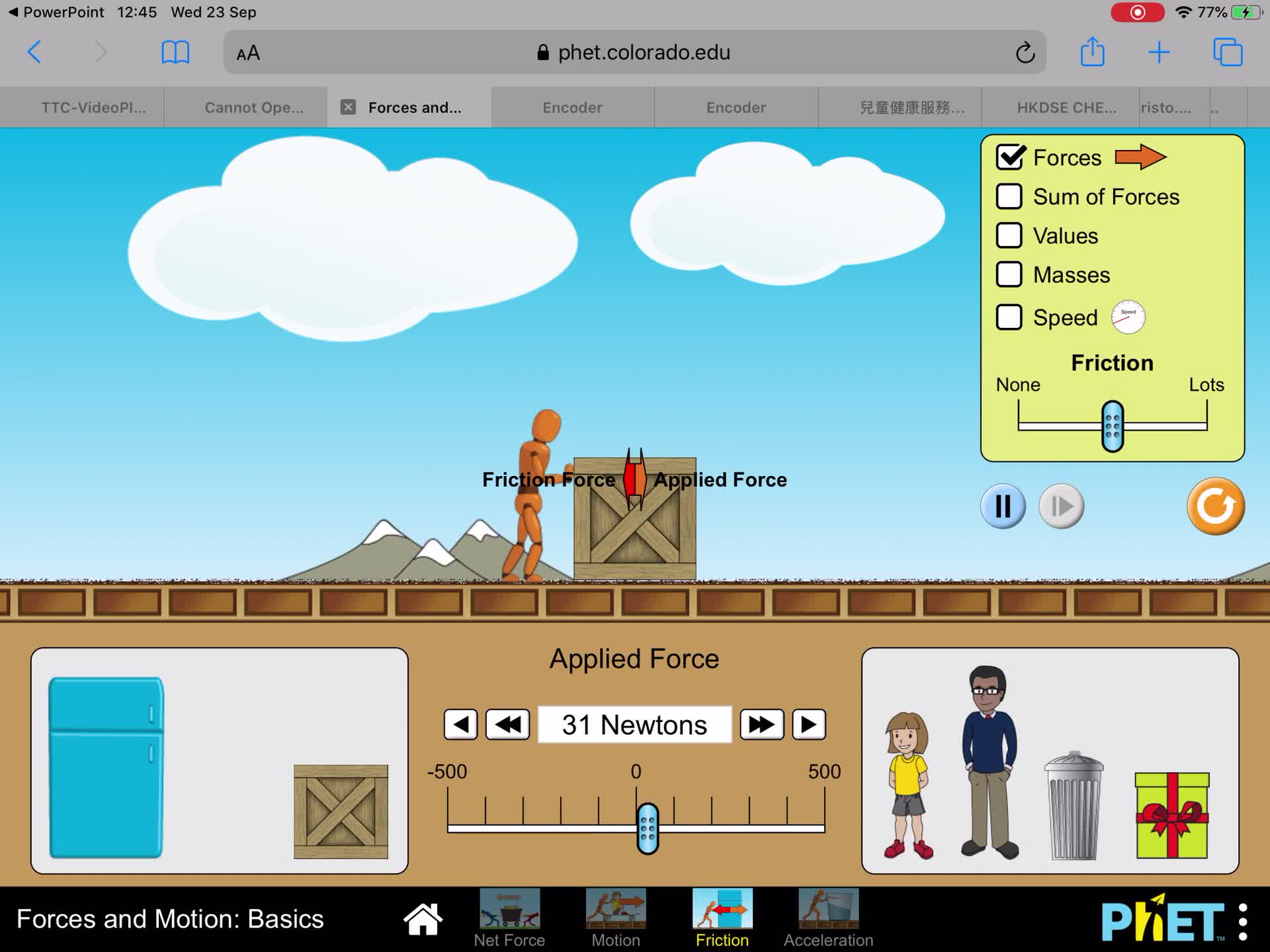
Friction


1A IS Unit 1 1.3 Part E
Free


1.3 B


1.3 C-D


1A IS Unit 1 1.3 Part C & D
Free


1A IS Unit 1 1.3 Part B
Free


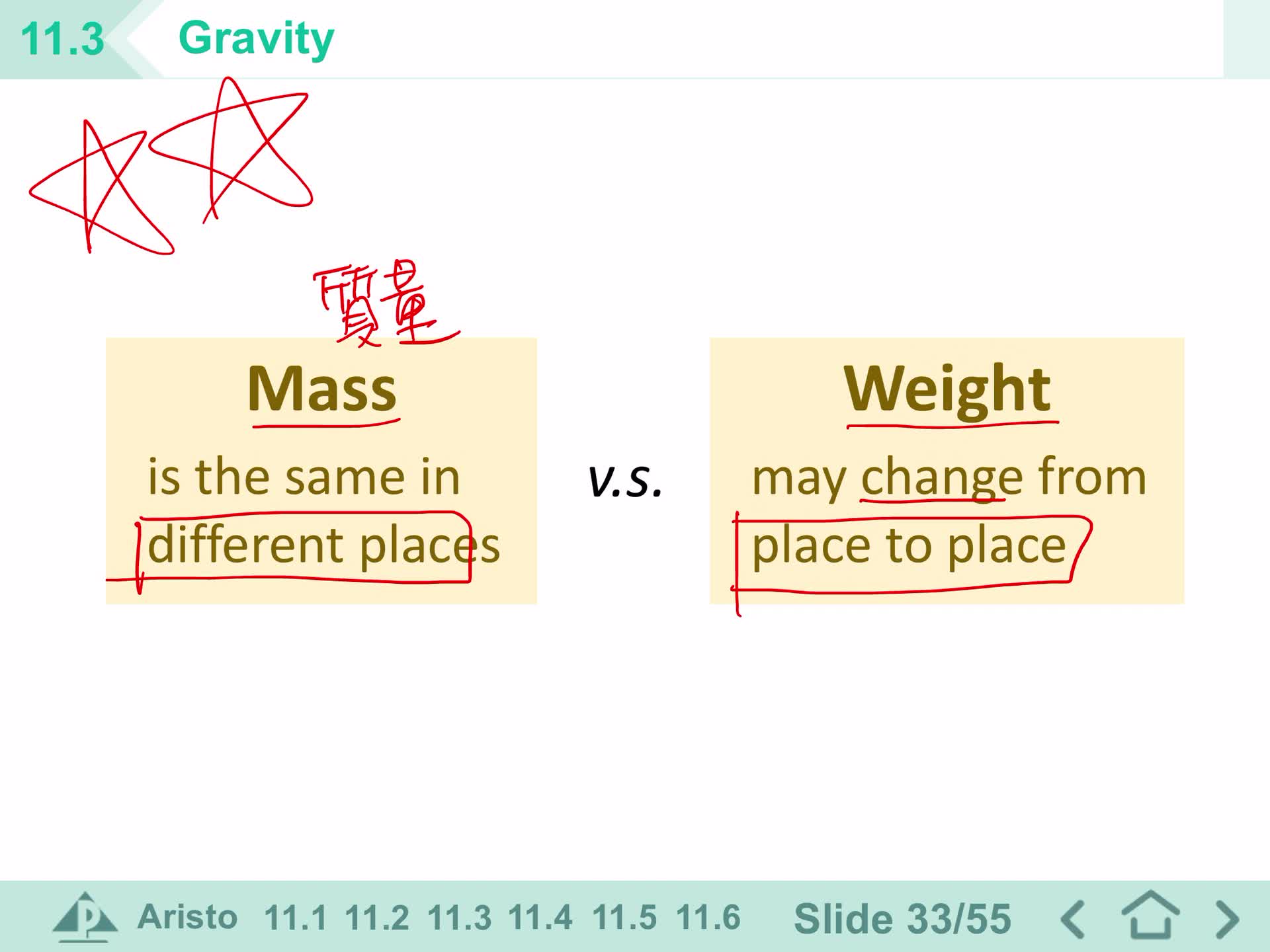
Mass & weight


Mass & weight


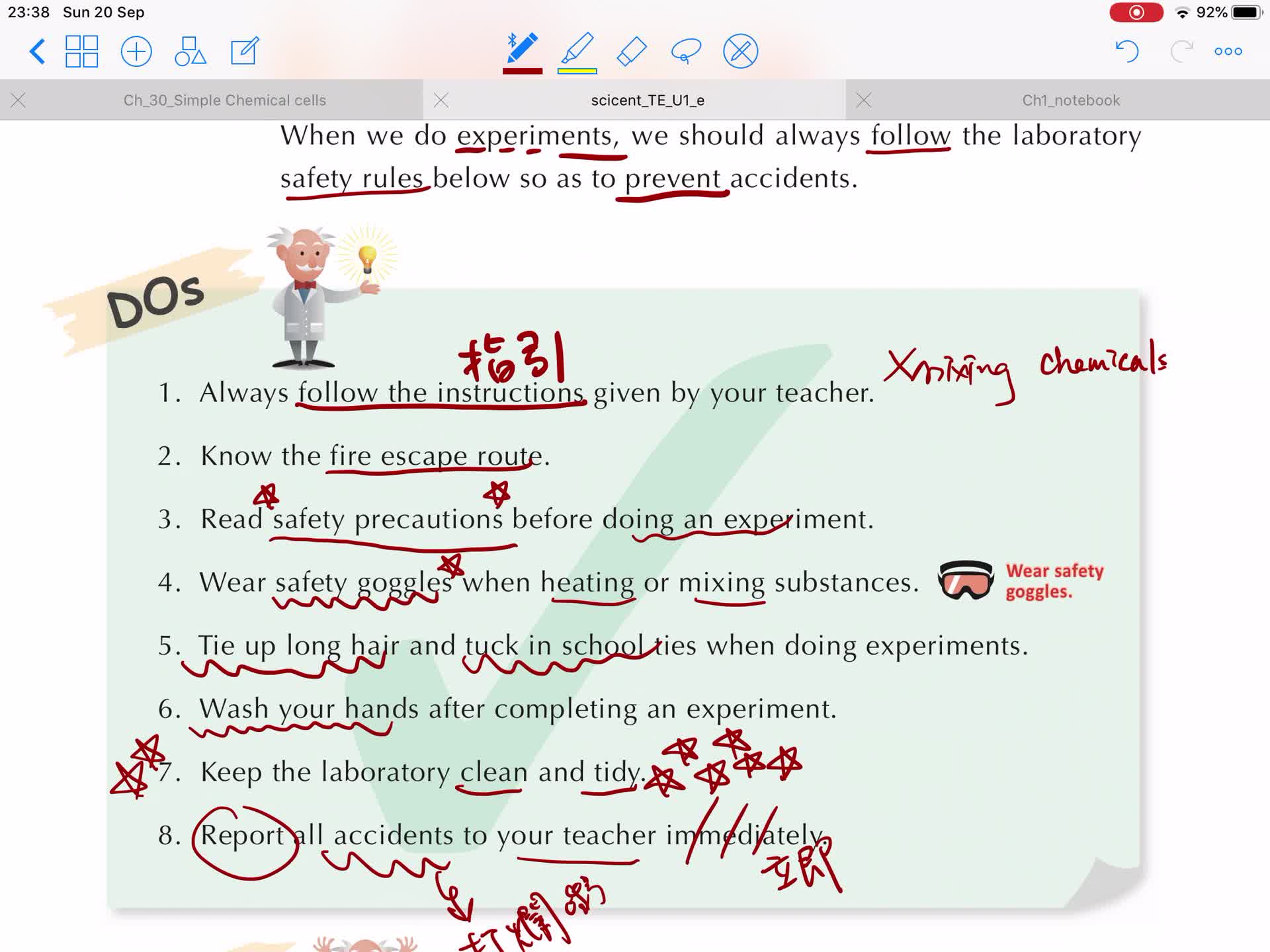
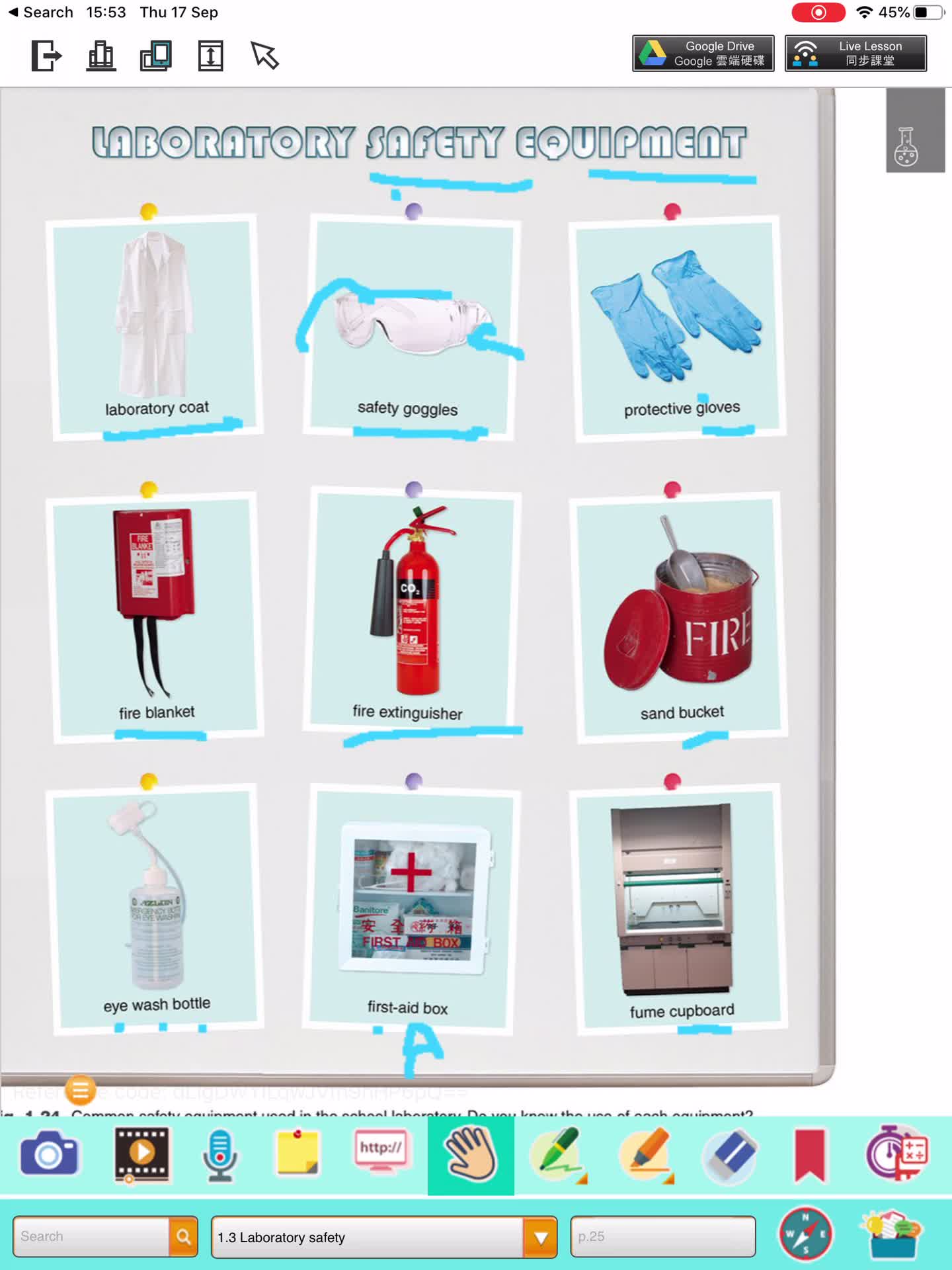
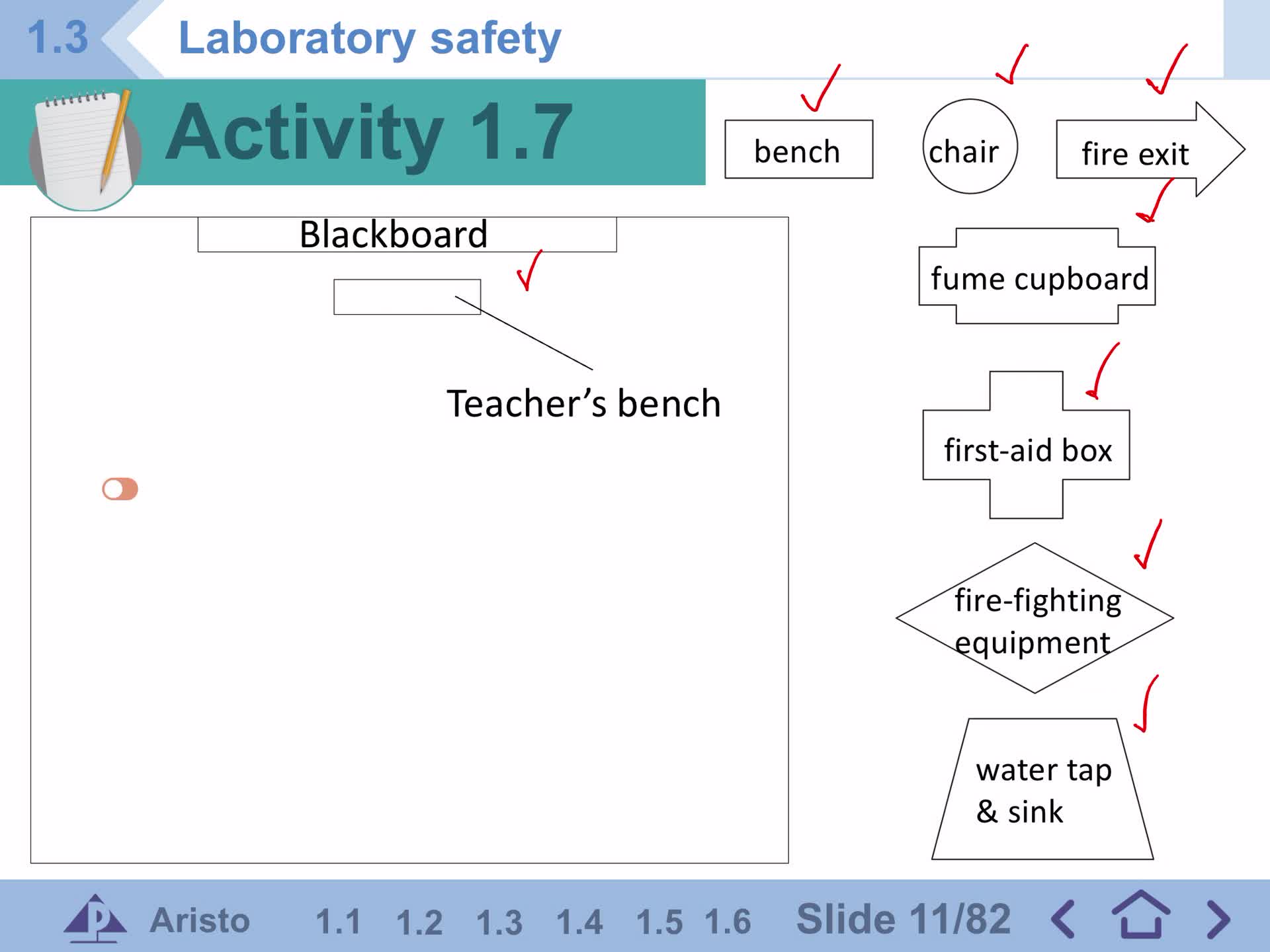
1.3 Laboratory safety


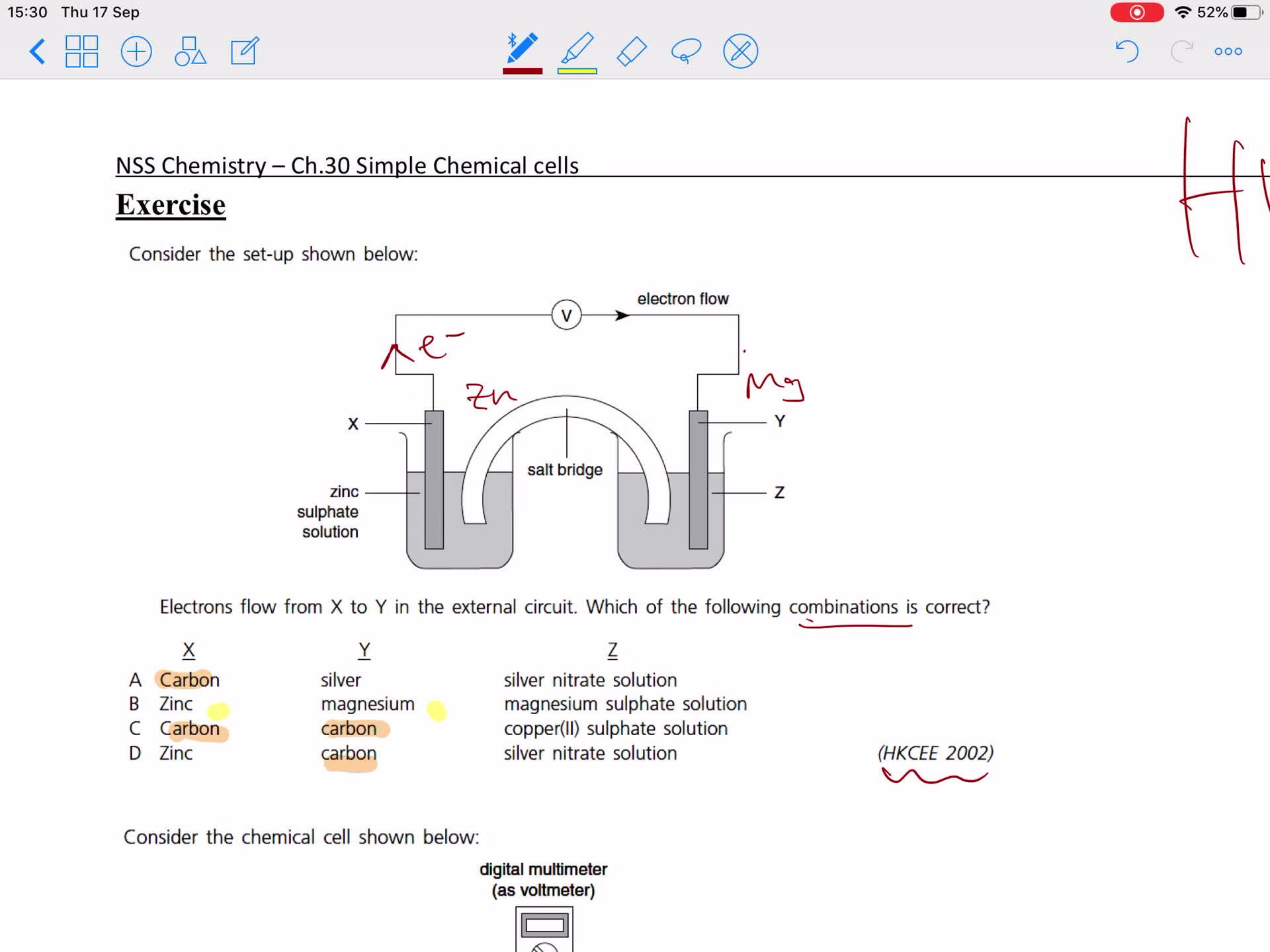
Sample questions of chemical cell


1A IS Unit 1 1.3 Part A
Free


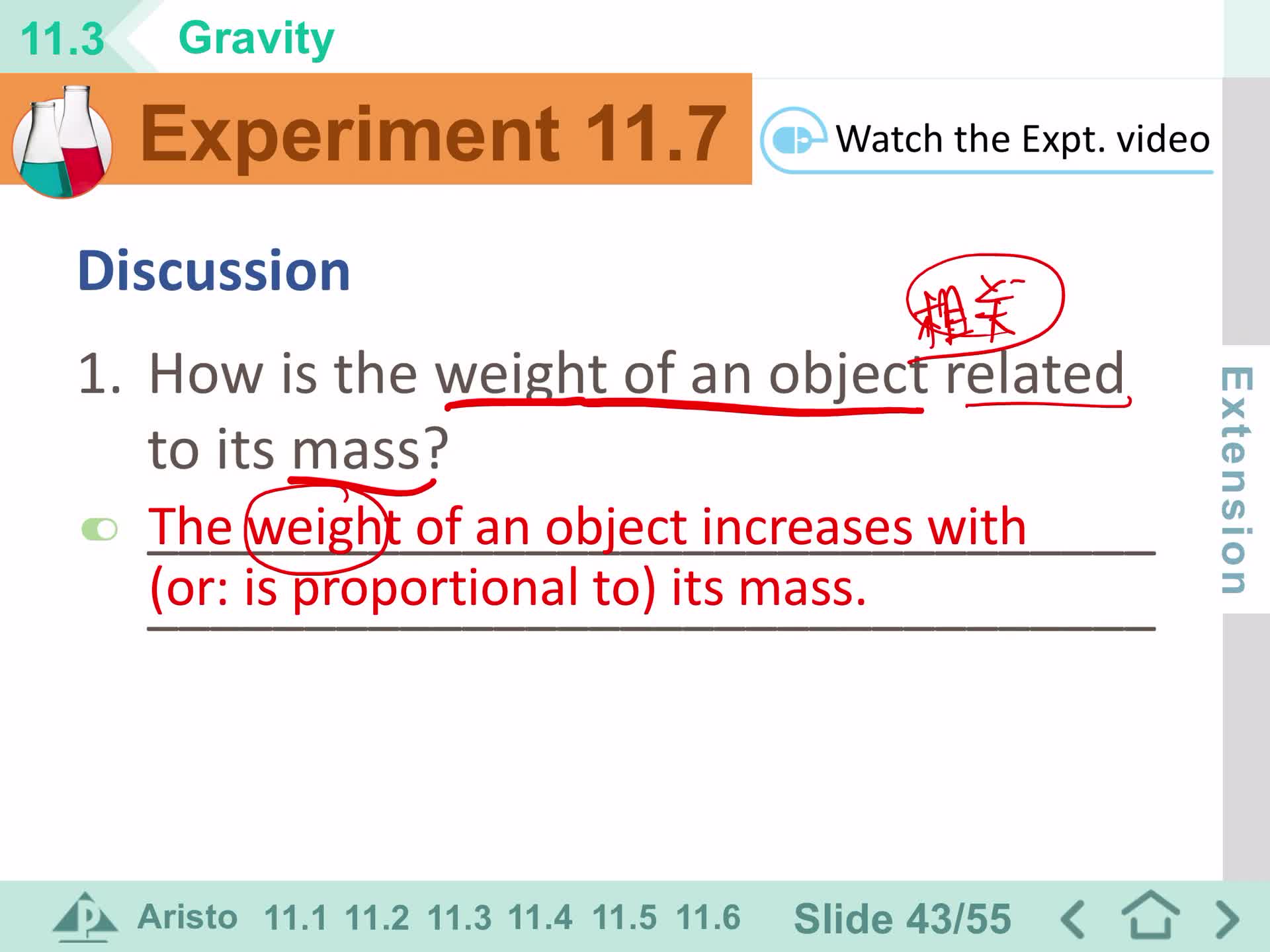
Force of gravity


Force of gravity


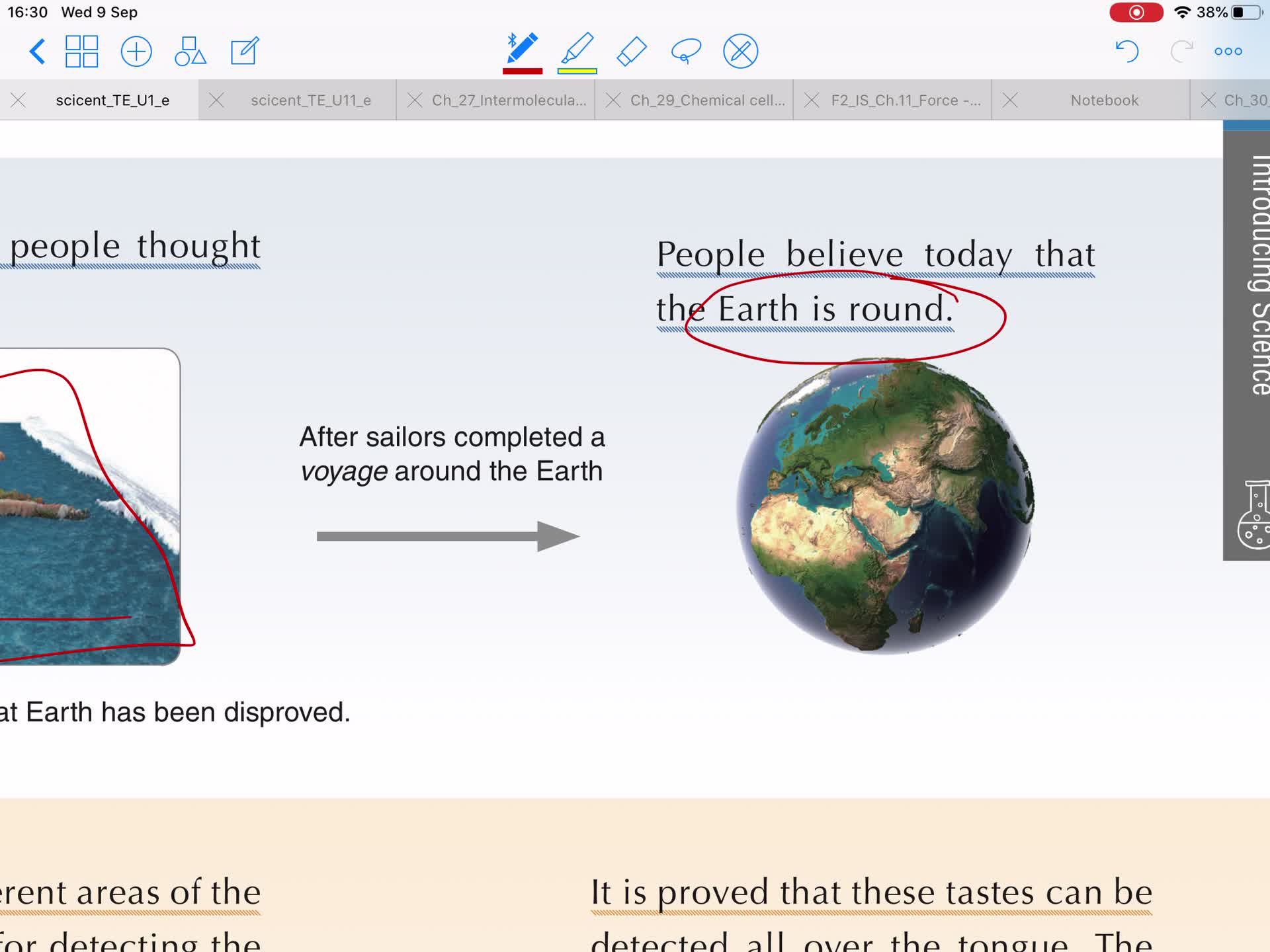
Classifying, pattern seeking & model building


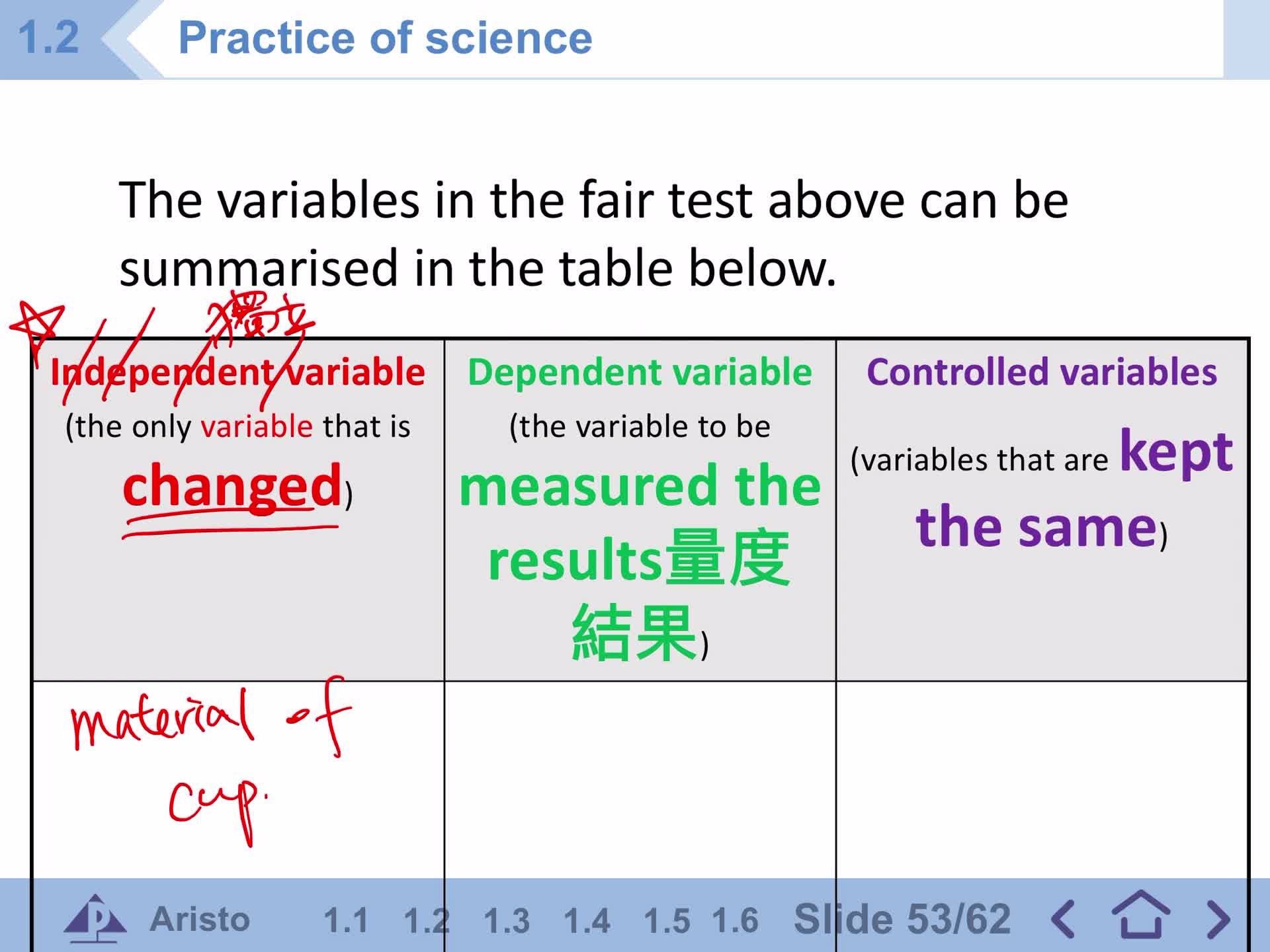
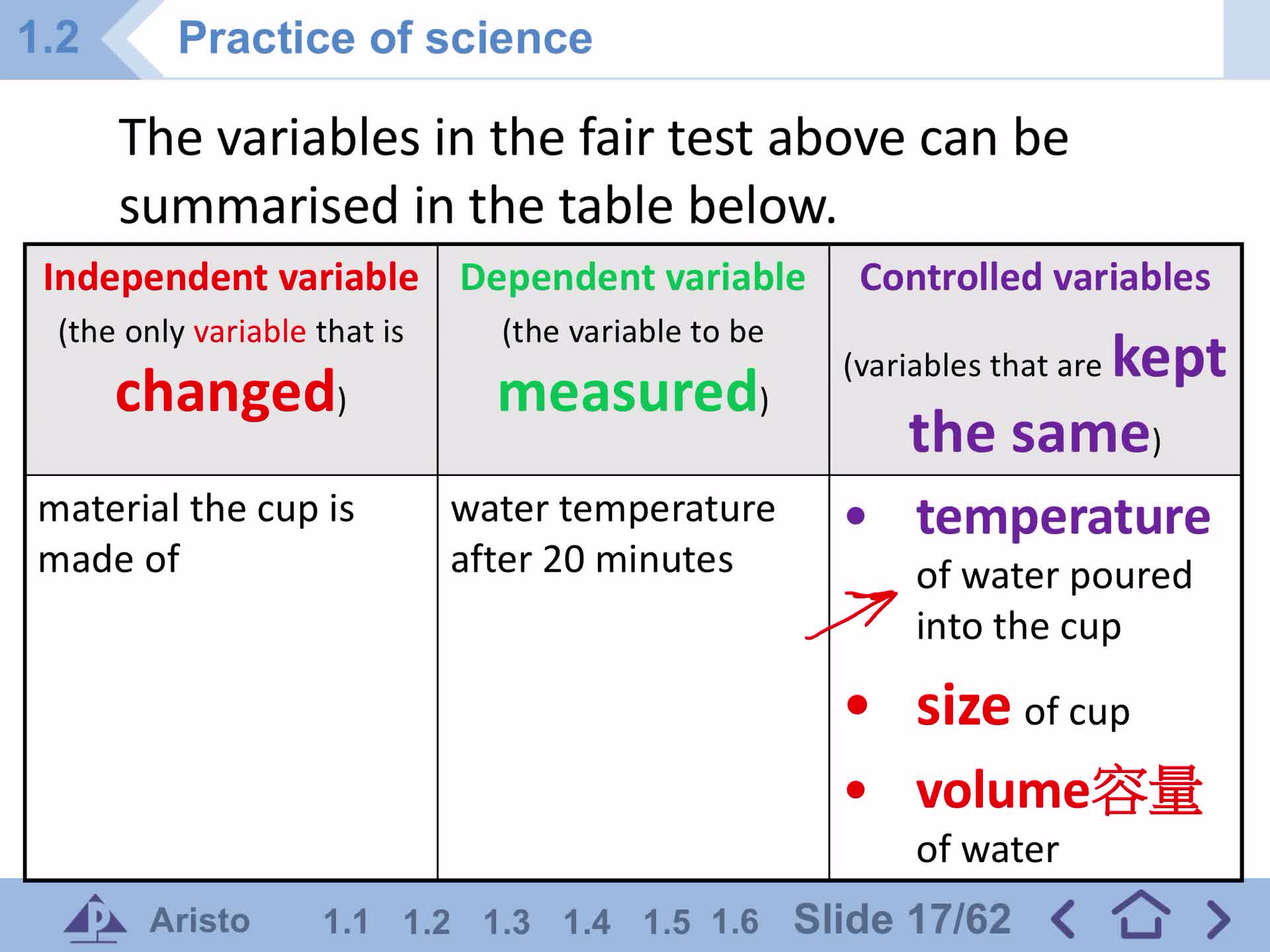
Fair test


1A IS Unit 1 1.2 Part B1
Free


1A IS Unit 1 1.2 Part A
Free


Steps of scientific investigation


Balanced force & unbalanced force II


Balanced force & unbalanced force


1.1 D


WB
Free


WB
Free


1.1 C2-4


9/9 Contact force & non-contact force(POW:F2is)


Balanced & unbalanced force (10/9)


1A IS Unit 1 1.1 Part D
Free


1A IS Unit 1 1.1 Part C (2-4)
Free


1A IS Unit 1 1.1 Part C (1)
Free


1A IS Unit 1 1.1 Part A & B
Free


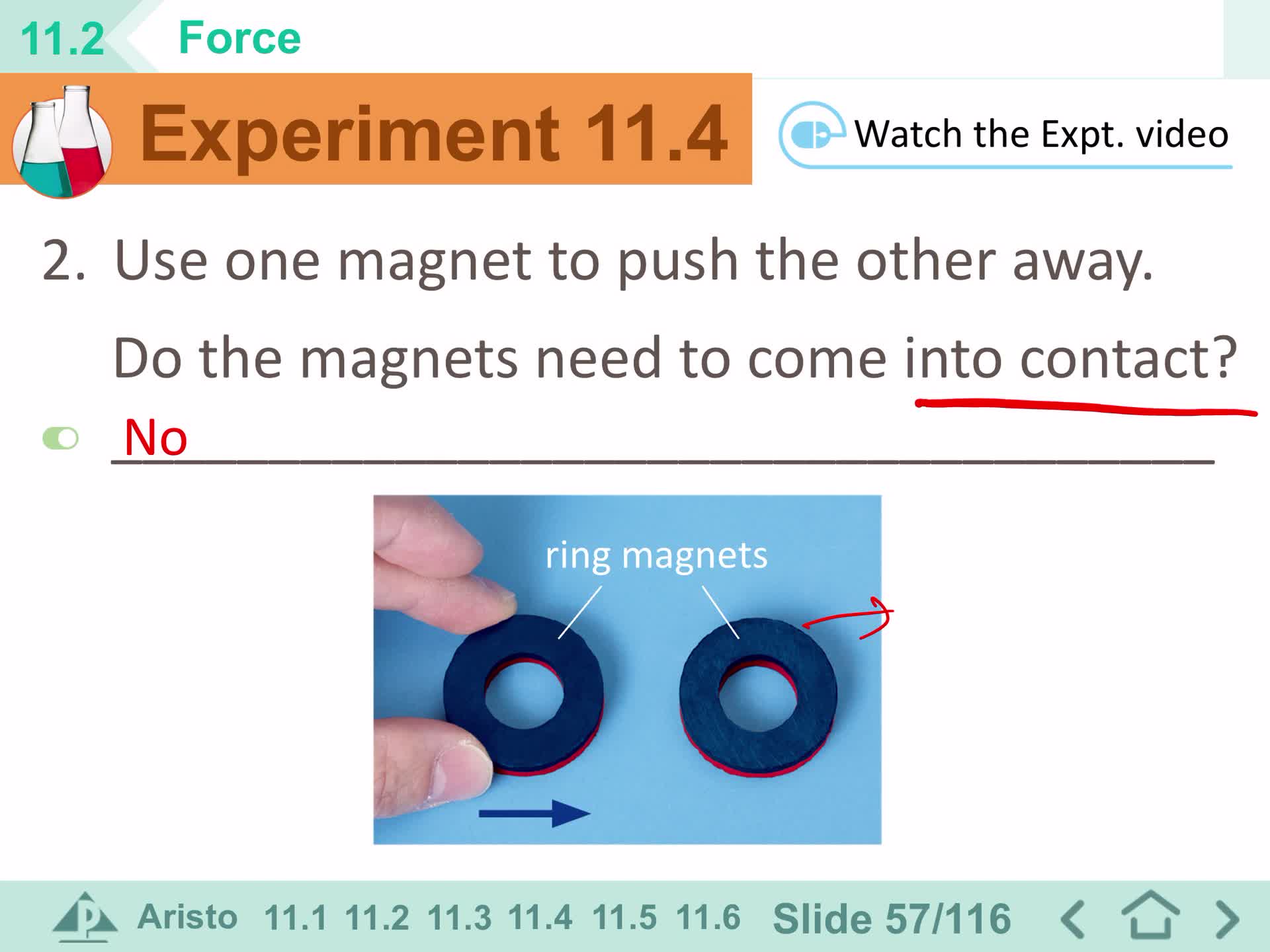
F2 IS Section 11.2 - force 1


F2 IS Section 11.2 - Force 2


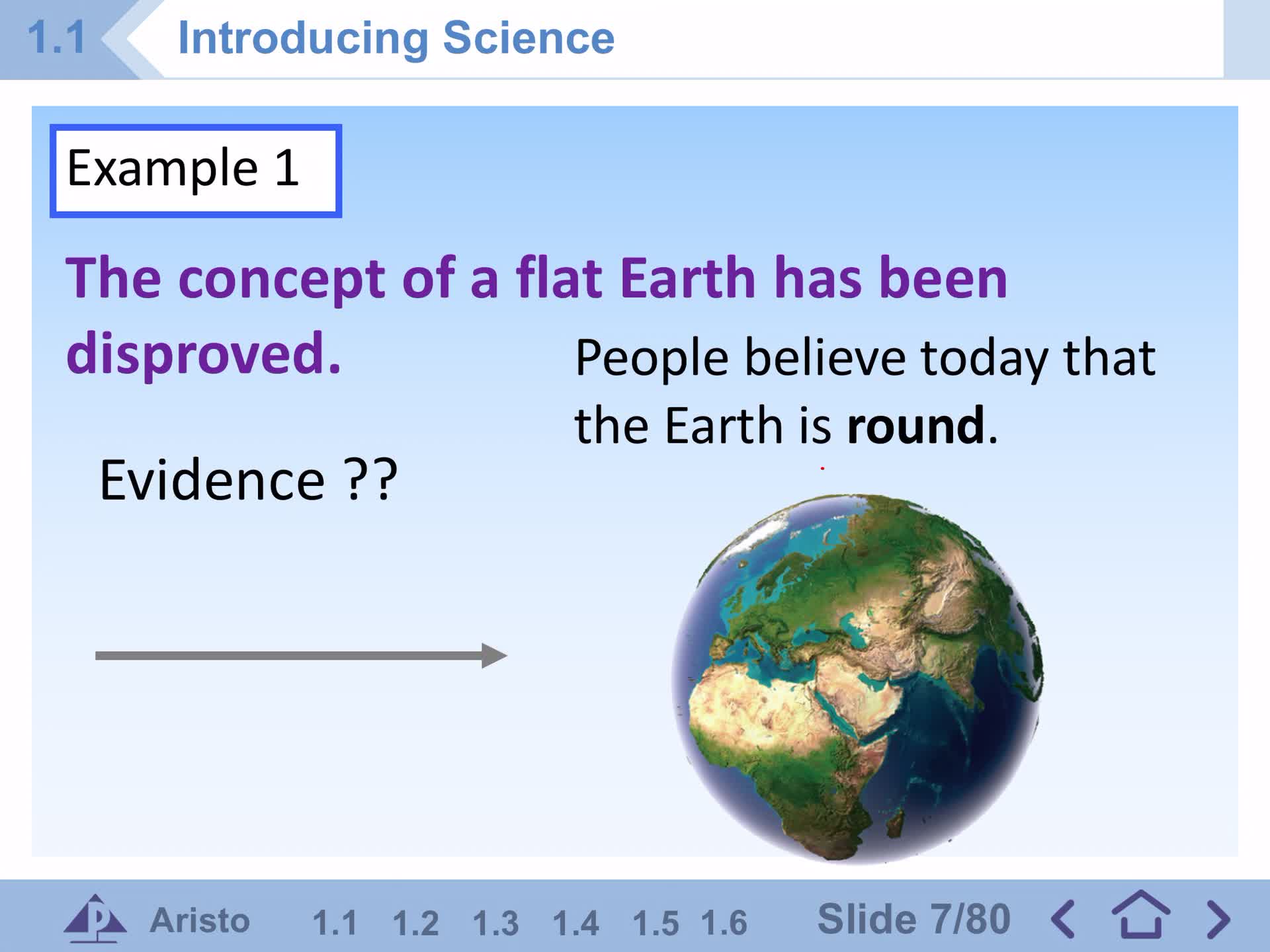
F1 IS Section 1.1 C1


F1 IS Section 1.1 A-B


20200528 F2 IS Video Class 40 (Part A)


20200528 F2 IS Video Class 40 (Part C)


Sec4-5BC


Sec4-5D


20200526 F2 IS Video Class 39(Part A)


20200526 F2 IS Video Class 39(Part B)


Sec4-5A


Sec4-4


20200525 F2 IS Video Class 38 (Part B)


20200525 F2 IS Video Class 38 (Part A)


20200522 F2 IS Online Class 37


20200521 F2 IS Video class 36 (Part A)


20200521 F2 IS Video class 36 (Part B)


Sec4-3C


Sec4-3D


Sec4-3A


Sec4-3B


20200519 F2 IS Video Class 35


20200518 F2 IS Video Class 34


20200514 F2 IS Video class 33


20200513 F2 IS Video class 31 (Part B)


20200513 F2 IS Video class 31 (Part A)


202005012 F2 IS Video class 30 (Part B)


202005012 F2 IS Video class 30 (Part A)


Sec4-1D


Sec4-1E


20200508 F2 IS Video class 29


20200507 F2 IS Video Class 28


20200506 F2 IS Video class 27


Sec4-1C


Sec4-1AB


20200505 F2 IS Video Class 26


20200427 F2 IS Ch.10 對作業


Sec5-3C


20200422 F2 IS - Ch.10 - HW (Part A)


Sec5-3A


Sec5-3B


20200403 F2 IS Video class 25


20200402 F2 IS Video class 24 (Part B)


20200402 F2 IS Video class 24 (Part A)


Sec5-2A


Sec5-2BC


Sec5-1


20200325 F2 IS Video class 22


20200324 F2 IS Video class 21


20200323 F2 IS Video class 20 (Part A)


20200323 F2 IS Video class 20 (Part B)


6-6C


6-6D


6-6AB


20200316 F4 Chem Online class 15 ( Part B)
Free


LEE YU F1 Ch6.4A


LEE YU F1 Ch6.4B


LEE YU F1 Ch6.2B
20200316 F4 Chem Online class 15 ( Part B)
479 0 05-Science Free
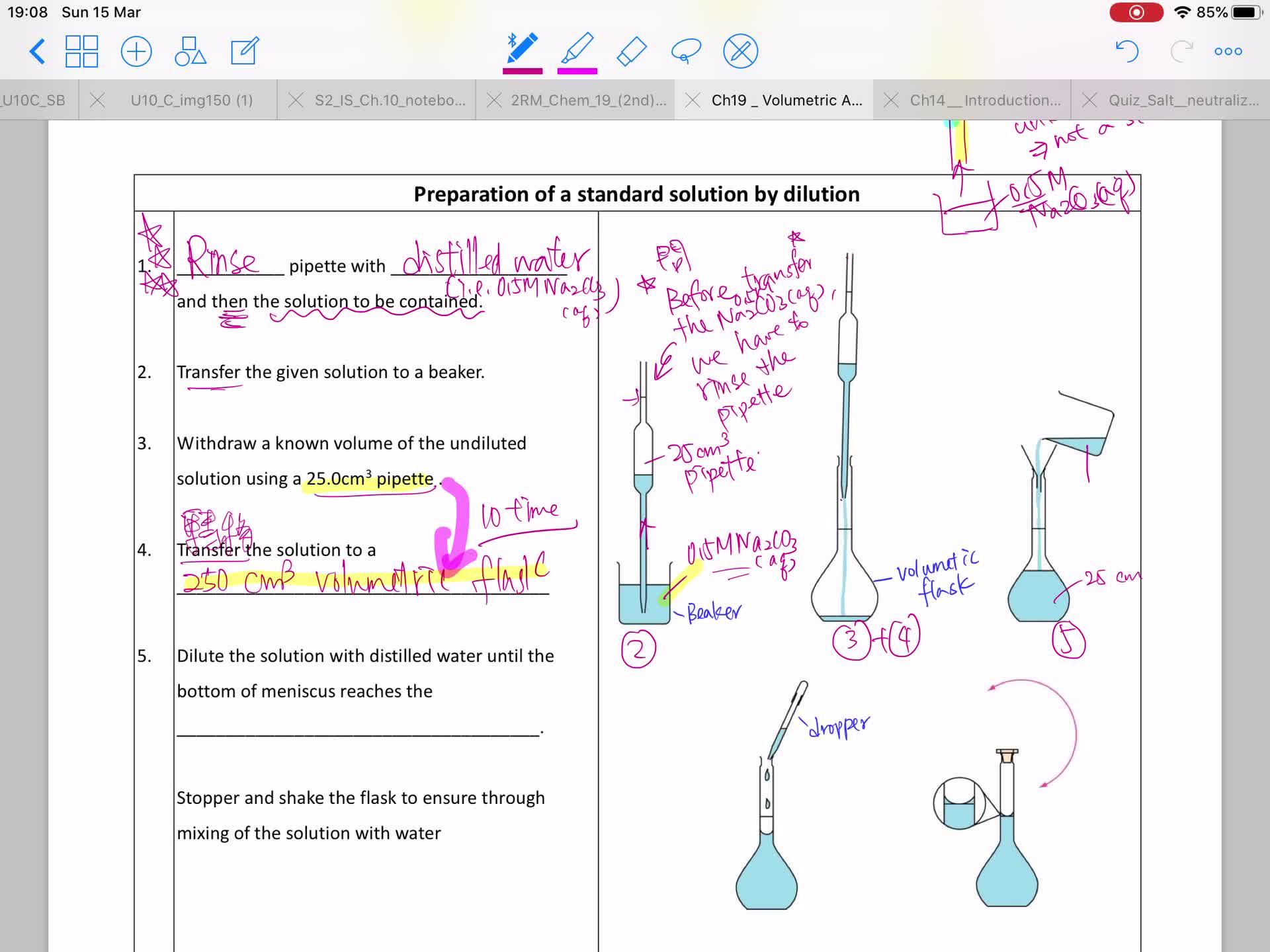
Ch.19 Preparation of a standard solution by dilution


LEEYU F1 6.2A


LEE YU S1 Ch6.1AB


LEE YU S1 Ch6.1C


3.5生物多樣性減少


3.6保育


3.4 生物多樣性


LeeYu F1 IS 3.3生物與生境


How to use schoology


Note P.4-5


S1 IS 檢索表


S1 IS 動物分類


S1 IS 脊椎動物分類


S1 IS 植物分類


S3 IS Expt Protease
Free


S3 IS Exp Amylase
Free


Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
Free


Human Digestive System for Testing The Video System
Free
Structure Of The Stomach - Functions Of The Stomach - How Does The Stomach Work
652 0 05-Science Free